Forward-thinking industrial IoT solution providers have made great strides in connecting their products and equipment to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). These providers produce sensors and industrial gateway IoT hardware to enable IIoT monitoring. This hardware allows users to combine smart things into IoT networks. Offering industrial IoT solutions and services, some of these providers:
- have built industrial IoT systems that collect data from sensors, process it, build trends, send alerts, and control sensors
- offer their customers platforms for centralized access to IoT networks and their troubleshooting
- add full-fledged modules that help to process business data collected from sensors for improved decision-making
If you fit into one of the categories above, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we view challenges, aims, and specifics of industrial IoT software development to cover your and your customers’ needs. These insights on industrial IoT solution development should help you ensure quality industrial IoT gateway design and build industrial IoT solutions that meet customers’ needs and expectations while minimizing technical and other associated risks. In this article, we also discuss IoT in manufacturing, agriculture, and other domains.
Before viewing the specifics of industrial IoT design, we need to differentiate IIoT and consumer IoT.
Read also: How to ensure remote management of large IoT networks


Differentiating industrial IoT and consumer IoT
Since this article is solely devoted to IIoT, let’s first figure out what IIoT is in comparison to consumer IoT. A consumer IoT network commonly encompasses several consumer devices. All of them have a limited lifetime of several years. On the contrary, an IIoT network is required to connect hundreds if not thousands of devices to maintain operations of costly industrial equipment over decades.
Below, we list the key differences between consumer IoT and IIoT. Take into account the peculiar properties of IIoT you see in the table while analyzing business requirements and developing technical solutions.

In the next section, we cover the main IIoT domains and their peculiarities.
Examples of problems IIoT helps to solve for different industries
While the word “industrial” may bring to mind warehouses, shipyards, and factory floors, IIoT technologies hold lots of promise for a diverse range of industries: agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and more. Let’s list some of the industries where industrial IoT automation is most prominent:
Agriculture. Using IIoT software helps farmers collect data on soil, nutrients, and moisture, using visual and thermal imaging to detect potential problems. One peculiarity of this industry is the large geographical area of the fields in which data is collected.
Manufacturing. IoT in manufacturing enables condition-based maintenance and data-driven process improvements. Using low-speed connections, automation, and digitized production, it’s possible to improve process and equipment stability, increase durability, and mitigate risks related to equipment malfunctions and violations of environmental norms.
Pharmaceutical. In the pharmaceutical industry, IoT devices can ensure condition and environmental monitoring throughout medicines manufacturing, storage, and transportation. This includes monitoring and maintaining air quality and ambient temperature requirements.
Mining, oil, and gas. IoT manufacturing solutions for the mining, oil, and gas industry can help control pumps and synchronize data from multiple sites. Usually, such solutions are used in a large production complex in which the team measures environmental indicators, performance indicators, and equipment depreciation.
Logistics. Using IoT, logistics providers obtain real-time visibility on cargo movement and item-wise monitoring so all items arrive where and when needed. IoT-powered warehouse management ensures real-time visibility regarding inventory levels, which helps to avoid costly out-of-stock events. IoT devices can also track the condition of an item and notify warehouse staff when temperature or humidity thresholds will be exceeded.
Each domain that is successfully adopting IoT technology is crawling with enterprises and managed service providers (MSPs). Many of them are considering developing their own IoT implementation initiatives, and here’s why.
Two types of target audiences for an IIoT vendor and how to satisfy their needs
The IIoT industry is advancing and expanding faster than many businesses realize. The pace of growth is revealed by research from MarketsandMarkets:
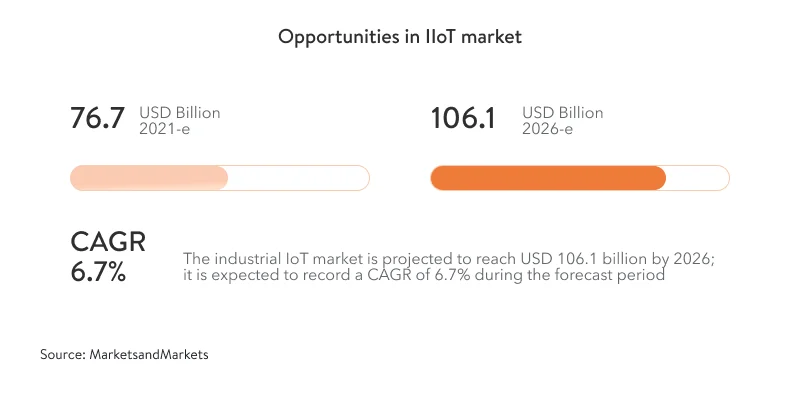
Enterprises and MSPs we talk about further in this article are essential contributors to this growth.
Enterprises with large IoT networks
IDC predicts a big jump in spending on IoT projects among enterprises in the coming years. In its worldwide IoT spending guide, IDC predicts global IoT spending will achieve a CAGR of 11.3 percent over the 2020–2024 forecast period. Such high demand provides great opportunities for IIoT vendors wanting to grow their business.
What service can you offer enterprises?
As enterprises prefer to adopt turn-key solutions, you can offer them an IoT management software ecosystem that consists of three layers:
- IoT hardware. This includes all physical components: smart devices, microcontrollers and microprocessors, physical casings, user interface components. Ensure a smart industrial design combined with an enjoyable user experience and supporting firmware capabilities to help target users deploy and perform basic analysis on the state of hardware devices.
- IoT software. This layer is used by end users, and thereby its development requires UI/UX design, mobile and web application development, and database creation. Also, implementing such a layer requires IoT product cloud development, as the cloud ensures access for all user roles.
- IoT connectivity development. This layer ensures connectivity between the hardware and software layers. The purpose of the IoT connectivity development layer is to maintain smooth and real-time data streaming between smart devices and the IoT software.
Keep in mind that each enterprise has strict requirements for functionality, reliability, transparency, auditing, and reporting. It’s essential to discuss such requirements during industrial IoT consulting. By the way, we provide such a service. If you want to learn what IoT services we offer, see our IoT-related expertise.
Managed industrial IoT services providers
According to Fortune Business Insights, the size of the global managed services market is projected to reach $557.1 billion by 2028 while demonstrating a dramatic CAGR of 12.6 percent between 2021 and 2028. According to Research and Markets, managed services will account for up to 71 percent of all enterprise deployments by 2027.
MSPs help enterprises adopt edge-to-edge and commercial-ready solutions on a large scale. At the same time, they offer the ability to scale on demand. In addition, MSPs enable enterprises to accomplish higher levels of digital transformation and improve their reach across external and internal supply chains.
What service can you offer MSPs?
MSPs are interested in building or improving existing platforms for IoT hardware monitoring used for data collection, processing, visualization, and device management. When creating such a platform for an MSP, take the following into account:
- If the MSP has several customers, they have numerous isolated IoT networks to monitor and manage via a single dashboard.
- Each end customer should only have access to their own network.
- The MSP should be able to separate data and reports for each of their customers (e.g. charge customers for a specific number of devices under service).
- The platform should meet requirements regarding IoT network monitoring, access, and management.
- The platform should provide a flexible permission model and access management for a multi-customer base.
- The platform should allow for UI customization (enabling an MSP Industrial Internet of Things company to add branding elements for a customer-facing portal).
To offer quality and customer-oriented services, you need to consider what customers expect from your services and their roadblocks on the path to adopting IIoT technology.
What problems do your potential customers face when adopting or using IIoT technology?
Challenge №1: Making use of huge amounts of data
It’s evident that when adopting IIoT technology, organizations start gathering large amounts of data. However, the matter of making use of this data to accomplish business goals is often left unresolved. Knowing how to use particular data to calculate and track particular KPIs is significant when adopting IIoT tools. When using these tools, lots of organizations just watch the amount of data grow while having no clue how to interpret it.
Solution: Implement IIoT network data analytics for improved decision-making
Data collected by organizations can be roughly divided into:
- business data (collected by sensors on things like temperature, level of dust in the air, and speed)
- data on the hardware network’s work (noise level, system efficiency, etc.)
All this data should be sent to a data processing center or be processed in real time for further decision-making.
It’s important to note that the way data is handled will depend heavily on the particular domain and use case. Here, we describe some approaches for dealing with IIoT data:
Data analysis and processing. Because IoT data comes in large volumes, performing real-time analytics requires the ability to ingest and enrich data with sub-second latency so that data is ready to be consumed in real time. There are many open-source analytics frameworks or industrial IoT platforms that can be used to provide IoT data processing and analytics for your IoT solutions. Analytics can be performed in real time as the data is received or through batch processing of historical data.
Read also: IoT data analytics and IIoT data management
Data storage. Data can be stored on-premises, somewhere in the cloud, or using a hybrid of these two approaches. Important considerations in deciding on the right data storage strategy are the data volume, network connectivity, and power availability. Another thing to consider is that different data is destined for different purposes. Data intended for archival purposes and data intended for real-time analytics can be stored using different approaches. Data access needs to be fast and support querying for discrete real-time data analytics. There’s also an emerging trend of edge computing to perform data pre-processing on-premises before pushing data to the cloud.
Data visualization. Visualizing data allows you to display big data in a meaningful way to better understand it. Visualizing data from multiple sources on a dashboard helps you make real-time decisions. Additionally, combining new IoT data transmitted from sensors with existing data can bring to light new business opportunities. You may also be interested in reading about data visualization in logistics.
Also, AI-powered and big data tools have achieved a good track record for ensuring data quality analysis, data visualization, and reporting. Depending on the use case, our Yalantis experts will help you choose the right tools for each of these approaches.
Challenge №2: Interoperability between systems in use
The most forward-thinking organizations have stopped leaning on legacy data systems and switched to modern software solutions like ERPs and MESs. Enterprises refuse to spend a fortune and a vast amount of resources on new tools that require closing gaps between systems. Therefore, such organizations are selective in choosing new software to make sure it’s flexible enough in terms of integration with existing systems.
Solution: Ensuring seamless industrial IoT integration into data systems by means of an IIoT integration service
To be competitive, you should offer your customers the easiest path towards innovation and allow organizations to make just a few adjustments in order to add intelligence, IoT devices, and automation on top of existing infrastructure.
Enabling communication between sensors and the internet requires middleware that provides interoperability all over a network by transforming data from one protocol to another. For instance, open platform communications (OPC) has proven to be effective communications middleware that ensures data sharing over networks, tackling interoperability challenges.
Challenge №3: Security risks
Along with its indisputable benefits, IoT has introduced some new security challenges. Growing security concerns, including software vulnerabilities and cyberattacks, can make lots of customers refrain from using IoT devices. Security incidents are especially harmful for companies operating in the energy, gas, oil, healthcare, finance, assembly, supply chain, and retail sectors.
The cyber attack on Oldsmar is a prominent example of the need for ensuring a high level of IIoT cybersecurity. In 2021, cybercriminals managed to access a computer monitoring chemicals used to treat drinking water for the city of Oldsmar. Attackers changed the level of sodium hydroxide from the normal 100 parts per million (ppm) to 11,100 ppm. Fortunately, the issue was promptly recognized, and normal operating parameters were brought back before any damage could be done.
The incident provoked reasonable questions. How did the industrial facility become accessible from the web? Why were remote access capabilities installed with no appropriate security policies and without reliable authentication? How could cybercriminals set process parameters to alarming levels with no additional authorizations and controls? Unfortunately, such incidents are common, and you need to take measures to protect your IIoT infrastructure.
Solution: Stepping up comprehensive security measures
IIoT infrastructure must be protected by a comprehensive set of security solutions that do not disrupt operations, reliability, and profitability. A simple and practical solution that can be easily and widely deployed is more effective than a superior solution that cannot be widely implemented. Security solutions should include the following features:
Secure boot. The cryptographic code signing techniques used in secure boot technology ensure that a device only executes code that has been created by a trusted entity (e.g. the hardware manufacturer). This technology prevents hackers from replacing firmware with a malicious set of instructions. If your IIoT chipsets are not equipped with secure boot functionality, it’s important to ensure that IIoT devices can only communicate with authorized services to avoid the risk of firmware being replaced with malicious instruction sets.
Reciprocal authentication. Cybercriminals can use a lack of reciprocal authentication to insert rogue or shadow IoT devices into the network and execute active and passive attacks. Based on the specifics of IIoT security scenarios and risks, device identity management and secure authentication is important. A security solution might include identity provisioning and management, network-wide key/credential management with proper automated rotation, and other mechanics. One more option is to use three-factor authentication frameworks that provide mutual entity authentication of the gateway with the remote user (subscriber) and the IoT node (publisher), along with session key generation. In three-way authentication, the central authority authenticates the two parties and helps them to authenticate each other.
Secure communication (end-to-end encryption). There are several schemes for exchanging, confirming, and periodically rotating encryption keys. These schemes were developed and tailored to IoT networks for ensuring reliable encryption during data transmission.
Security monitoring and analysis. It’s important to ensure that end devices are protected from possible hacking and data manipulation, which can lead to misreporting of events. After collecting data about the overall state of the system through security monitoring, this data is analyzed to identify possible security breaches or potential system threats.
Cybersecurity certifications. IEC 62443 is a set of internationally recognized industrial IoT standards that establish the operation and product requirements for the secure development of IoT in Industrial Automation and Control Systems.
For more on the topic, read about our cybersecurity expertise.
So far, we have given a brief analysis of the business context and target audience for IIoT devices, the needs and challenges of the target audience, and some tips on how to overcome them. Next, we share solutions that will help you create IIoT software fast and securely.
Before diving into the niceties of IIoT software development, we want to mention that we can offer team augmentation services for your IoT project. Check out our case study on one such project.
What to consider during IIoT platform development
Based on our extensive IoT software expertise, we can help you create sophisticated industrial IoT solutions and services to optimize maintenance, enhance secure data collection and transfer, and improve operations with a meaningful solution on top of your existing IoT infrastructure. While building IIoT software, we take into account the following:

Enabling flexible remote setup. Building a remotely controllable cloud platform is a great solution for simplified setup and maintenance of large IoT networks. Such a platform will enable you to simultaneously set up, synchronize, and replace hardware. To provide remote management, use dedicated IoT protocols like LWM2M or MQTT. Using such protocols will also let you seamlessly integrate your IoT solution with your own and third-party systems if needed. We created such a platform for remote IoT device management. This is a SaaS solution that improves setup and maintenance of large IoT networks.
Ensuring business continuity. In the context of developing industrial IoT solutions, business downtime is expensive and unacceptable. That’s why sufficient flexibility must be built into both the equipment and the remote control system. For example, easy device replacement, enhanced monitoring, and alerting features must be provided with the number of devices in mind. You can read more on this topic in one of our recent articles. You may also find more information and best practices in our article about remote management of large device networks.
Enabling bulk operations. As large IoT networks are common for IIoT, you’ll need to develop logical entities that will combine different IoT devices for provision of bulk operations (device onboarding, firmware updates, etc.).
Providing multitenancy. As MSPs manage multiple customer deployments and provide customer teams with access to the same remote management monitoring system, multitenancy is a critical security and architectural requirement. Making sure that assets and data are properly isolated and visibility is strictly managed is a must.
There is no benchmark for IoT development and designing an industrial IoT architecture, as the industry is young and developing. Therefore, for industrial IoT companies, it’s important to find a software provider with relevant expertise. Yalantis is one of the IoT platform companies with experience building solutions to optimize equipment maintenance operations and enable visibility in asset use. Get in touch if you want to create or improve your IIoT software.
FAQ
What are industrial IoT monitoring use cases?
IIoT monitoring cases vary and can deliver an array of benefits depending on the company and what IIoT monitoring is used for. The most common use cases include predictive maintenance to prevent costly equipment’s breakdowns and repairs, reducing energy usage by optimizing the use of equipment and/or production, and quality assurance of resources and products.
What are the types of industrial IoT platforms?
The ability to manage and supervise industrial IoT devices and data they provide is the main benefit of using an IIoT platform. However, such platforms vary by capabilities to be useful for different use cases. Actually, it would be an exaggeration to say that there are specific types of IIoT platforms. Rather, IIoT suppliers are expanding their platform capabilities to satisfy growing clients’ expectations and particular business needs. Modern IIoT platforms provide users with a different mix of capabilities including IIoT endpoint management and connectivity, data ingestion and processing, and data visualization and analysis.
Why choose Yalantis for IIoT software development?
We are experienced in IoT platform development, cloud IoT migration, and enabling IoT analytics. Specifically, we build IIoT network management platforms for IoT suppliers who target managed service providers and large manufacturers. Check out our IoT expertise, case studies, and clients’ reviews to explore our polished IoT software development processes, our IoT products’ capabilities, and the project results.
Rate this article
4.1/5.0
based on 37 reviews







