Edge computing is a new way to look at data management from anywhere possible, even from space. NASA is already tapping into edge computing to protect astronauts from dangerous diseases. IoT on the edge is especially useful for industries where seconds matter and the cost of delay is extremely high, such as in healthcare, manufacturing, green tech, smart cities, telecommunications, logistics, and agriculture. Edge computing allows businesses to keep a close eye on their operations and constantly process real-time feedback from IoT sensors.
According to Statista, the edge computing market will reach $274 billion by 2025 as compared to $176 billion in 2021. In this article, you will find answers to the following questions:
- What is IoT edge computing?
- What’s the reason for the increasing popularity of edge computing?
- How and when can IoT companies benefit from edge computing?
However, we want to address the most common misunderstanding right away: edge computing for IoT doesn’t completely replace the cloud. In fact, it’s possible to use both to achieve all-around control over all business processes.


Differences between cloud and edge computing
Cloud and edge computing aren’t rivals and often complement each other. In fact, such cloud hyperscalers as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud want to have their share in the edge computing market and offer lots of solutions and platforms to integrate into IoT networks. In this way, they want to maintain their existing customers and attract new ones.
But how exactly are cloud and edge computing different? The first and most obvious distinction is the proximity to the data sources (e.g. IoT devices), with cloud data centers being far away and edge servers located as close as possible. Let’s have a look at the table below, where we’ve listed critical differences between cloud and edge computing.
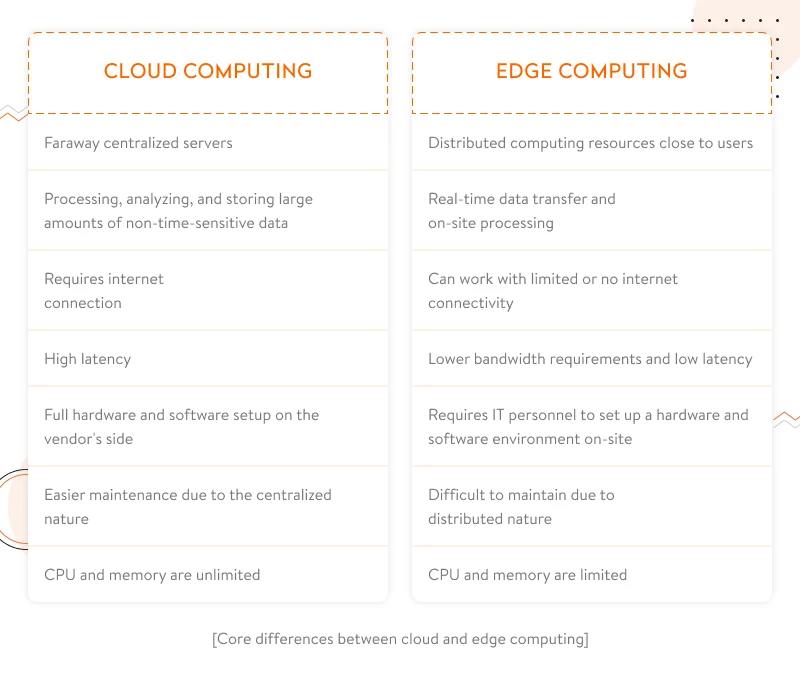
Thus, we see that edge and cloud computing serve completely different purposes. When you don’t need your system to respond in real time to make quick decisions or provide your customers with immediate services, you can have only a cloud connection. However, if real-time data processing is crucial for your business to function properly, then edge computing is your go-to. But remember that edge computing still requires cloud computing as an orchestration center to control the work of edge nodes and IoT edge devices.
The most common limitation of edge computing in IoT is that edge devices can process only those tasks that can be distributed across edge resources. Some tasks, such as business logic analysis, can’t run in parallel in the distributed environment and have to be processed in the cloud only.
The edge layer serves as a filter for your business-critical data. Edge nodes can also process certain time-sensitive data but send to the cloud only the result of this processing. For example, IoT sensors installed on a compressed air system in an industrial facility can constantly assess the system’s state. Imagine an IoT sensor spots an issue, then transfers information about this issue to the edge node installed in the same facility for immediate processing. Then the facility worker gets notified of the issue via a certain web portal to take immediate action. That’s edge computing.
But after the action is taken and the system’s work has resumed, the edge node can send to the cloud a brief report on when the issue happened and how quickly it was resolved so that data analytics later conduct thorough analytics on how often the system fails during a certain period of time and how it affects business costs.
When it boils down to the IoT domain, using both cloud and edge computing can be beneficial. Let’s find out more about edge computing in IoT.
How the IoT industry can benefit from edge computing
IoT and edge computing are intertwined. But what is an edge device in IoT? An edge device is actually an umbrella term for all IoT devices and sensors located at the edge, meaning near end users. As IoT Analytics reports, in 2022, the number of IoT devices will reach 14.4 billion, and by 2025, a whopping 27 billion. Imagine how much data these devices will generate.
Edge computing can come to the rescue in significantly optimizing the data management of large IoT networks. Often, it’s inefficient to send a lot of data to the cloud. It would be much better to process data on edge nodes and transfer to the cloud only data necessary for long-term storage or that requires computationally demanding analysis that limited edge hardware can’t deal with.
Common IoT edge computing benefits include:
Low-latency and high-bandwidth communication
An edge computing gateway is located close to IoT devices, and this proximity guarantees quick data transfer from an IoT edge device to the gateway. Edge computing is especially beneficial for bandwidth-intensive data, such as for videos from surveillance cameras. Imagine sending lots of video data (often practically the same) every second to the cloud storage. This would be unreasonable as well as cost- and time-intensive.
For instance, when a road traffic camera spots a car accident, it’s necessary to transmit data to the traffic management system right away. Sending this data all the way to distant cloud centers for processing would take a long time, and by the time the system got the message, it could be too late. Such emergency situations require immediate action.
Distributed computing resources
Edge computing resources can be distributed across any location, such as an industrial facility or even an agricultural field, and gather data from the whole distributed network of IoT edge computing devices. In such a manner, edge computing allows you to cover large working areas and monitor performance and productivity in real time at every site. To dive deeper into real-time data processing, check out our extensive guide.
Security and compliance
Local distribution of edge servers makes it easier to ensure compliance with local laws and regulations. And since most business data is processed locally on edge nodes, you can avoid data interception while sending sensitive data (such as health information) to the cloud.
Sustainability and cost-efficiency
Implementing an edge layer in your IoT network can also ensure better sustainability and cost-effectiveness for your business. With edge computing, you can reduce costs on cloud resources, using them only when necessary. Plus, as edge computing enables immediate data processing near IoT edge devices, you can make use of predictive maintenance. For instance, edge computing can allow for preventing oil or gas leaks that severely damage the environment or help you cost-efficiently and energy-efficiently use industrial equipment by defining its optimal operating time. Predictive maintenance in IoT is a vast topic, and if you’re interested, make sure you read our article on ensuring IoT predictive maintenance for large manufacturers.
Being in more control of the work environment thanks to the combination of edge computing and IoT naturally pays off in reduced capital and operating expenses and has a positive impact on the environment. In particular, large manufacturers cause a huge amount of environmental damage. The Emissions Gap Report 2022 by the United Nations environment program offers critical actions to take to achieve industry transformation in terms of better sustainability:
- Full decarbonization of industrial production
- Reduce material waste and recirculate materials
- Enhance access to energy-efficient materials
Edge computing can be an effective way to facilitate those actions. In the next section, you’ll find out how edge computing solves typical IoT challenges.
5 IoT challenges to solve with edge computing
We’d like to highlight five challenging IoT scenarios you can overcome when you opt for edge computing.

Edge computing in IoT is a great way to streamline and speed up your business operations, ensuring greater customer satisfaction as well as a more productive workplace for your employees. Now, we can figure out what IoT edge computing benefits and challenges can look like in practice.
Read also: How an IoT provider can ensure remote management of large IoT device networks
Typical edge computing IoT examples
In this section, we take a look at industries that can especially benefit from edge computing.
Manufacturing. In case of any unexpected outage or issue, processing on the edge can save you much time and money by either predicting system malfunctions or notifying you in case any critical issue has occurred. If you’re a large manufacturer, you can also consider exploring our in-depth article on IIoT data management and analytics.
Agriculture. Monitoring crop growth and soil characteristics with sensors and then transmitting this information for real-time analysis can help farmers keep a close eye on their business and maintain a stable harvest. Since IoT edge devices can work without an internet connection, it’s possible to place edge nodes even in the most remote and hard-to-reach locations.
Healthcare. Remote patient monitoring and diagnostics, robotic surgery, and immediate emergency response are life-saving examples of edge computing applications in the healthcare industry. Healthcare practitioners can have a bird’s-eye view of their patients’ health and monitor it around the clock. Plus, thanks to edge computing, it’s possible to maintain large amounts of extremely sensitive health information within the premises of the healthcare facility.
Smart city. A large distributed network of smart devices across large cities allows edge computing to reveal its full magic. With edge computing, city authorities can maintain control all over the city and immediately react in case of emergencies or even take proactive measures in response to potentially hazardous situations.
Green tech. Lots of green tech companies, including those that offer EV charging, are also making use of edge computing due to its real-time computational capabilities that enable quick response times in the most critical situations. According to PwC, there will be almost 27 million EVs in the US by 2030. To meet the needs of such a large number of drivers, the EV charging market is expected to grow tenfold. Edge computing is among the crucial technologies that can facilitate the rapid evolution of the EV charging domain.
Let’s have a look at the basic edge IoT architecture of an EV charging management system with an edge computing layer to more easily grasp the interactions between EV charging and edge computing.
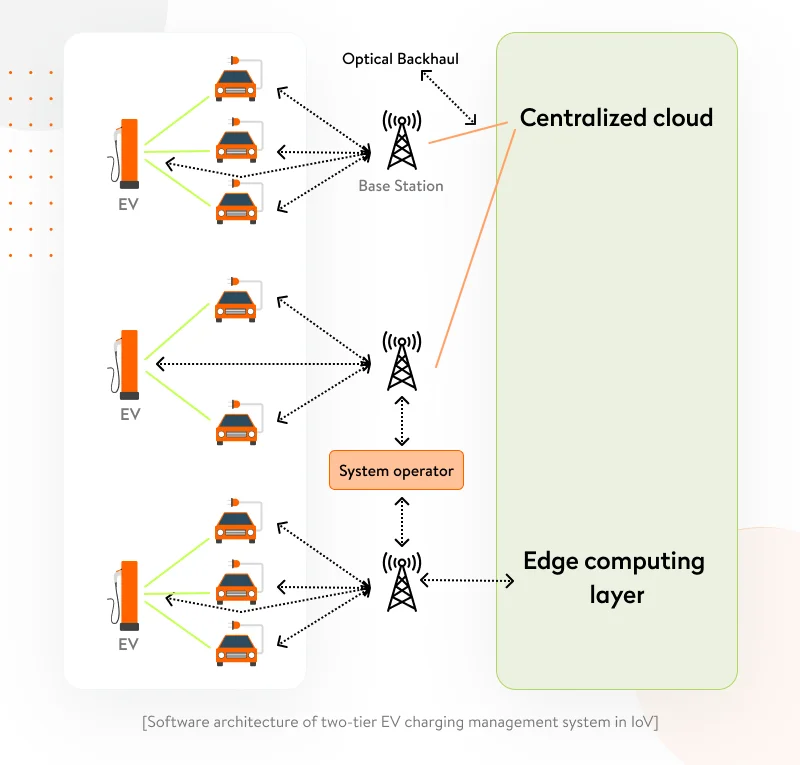
Thanks to on-hop wireless communication between edge nodes, EV charging stations can quickly transmit:
- real-time data on their performance
- their critical operating properties
- the number of drivers that charge their vehicles in a day
- lots of other important information to maintain proper round-the-clock functioning of the charging station.
Such high performance can be partially achieved using fast and progressive programming languages like Rust. You can find out more about this language in our Rust market overview.
Edge computing infrastructure can also help EV charging businesses tackle two critical needs:
- Efficient energy management. It’s cumbersome to manually calculate each charger’s energy consumption as well as constantly ensure that every driver will have a chance to charge their EV even during peak hours. Edge computing can help maintain the stable workflow of each charging station regardless of its location.
- Massive data processing. A wide network of EV charging stations generates large amounts of data every second. Combining a centralized cloud environment and a distributed edge computing infrastructure can help the network efficiently process large amounts of data.
Of course, this list isn’t exhaustive, as edge IoT is a broad topic and there are many methods for its implementation. Before edge computing came into our lives, we were losing lots of tremendous opportunities to go beyond our human capabilities. But how can you learn whether it’s worth investing in such a solution? Let’s find out in the next section.
Read also: How can IoT suppliers build industrial IoT software to attract new customers
Checklist: When do you need edge computing in IoT?
We’ve already discussed the common benefits of edge computing, IoT challenges it can help to tackle, as well as typical use cases for edge computing including the IoT edge architecture. Now, it’s time for a short checklist that can help you decide whether edge computing in IoT is the right choice for your business. Below, we describe seven possible scenarios when edge computing can be your go-to.
- When you see the necessity for real-time data analytics to ensure a better level of visibility within your organization with IoT edge services and cloud computing isn’t enough to fulfill these purposes
- When the low latency millisecond response times that IoT on the edge can provide are important for your business and can help you improve the customer experience
- When you need to ensure less human intervention for your business processes to run smoothly and want to implement efficient remote management and monitoring of your IoT network
- When you want to ensure the highest level of business continuity and eliminate outages of your business-critical applications and devices
- When your organization generates large volumes of data and the distributed nature of data storage and processing that edge computing offers can be beneficial
- When it’s critical for you to ensure the security of your business data locally and reduce the chance of fraudsters intervening in your edge IoT devices
- When data sources at your organization are distributed across a large working area
Even if only one of these scenarios suits your business model, it still means that edge computing infrastructure can be highly advantageous for your business.
But empowering your organization with edge computing can be a difficult task and requires your IT team to have substantial R&D skills. Partnering with true professionals in IoT edge solutions can save you lots of money and time in the long run. At Yalantis, we provide diverse IoT services, from team augmentation and consultancy to development of full-fledged IoT software. Consider investing in a custom edge computing solution and give new life to your IoT network to start reaping the benefits from real-time data processing now.
Need maximum business productivity at the IoT edge?
We’re here for you.
FAQ
What is edge computing in IoT?
Edge computing in IoT is a way to use distributed computing resources as close as possible to IoT devices or sensors. A distributed edge infrastructure allows for quick data collection even without an internet connection and regardless of the geographical location of the IoT devices and edge gateways. When data is collected, edge servers can process it in real time as well as conduct preliminary data analysis necessary for quick business decision-making and efficient customer service.
How does IoT edge computing differ from cloud computing?
Cloud computing and edge computing work on different levels of the IoT architecture. The cloud stands at the top of the hierarchy and is responsible for big data analytics, long-term storage of business and customer data, as well as monitoring operations on lower layers including the edge layer. Edge computing takes place close to IoT devices and end users and is responsible for local data management to enable proper business functioning at the operational and tactical levels.
How can different businesses benefit from edge computing in IoT?
General benefits include an improved customer experience and services, increased sustainability and energy efficiency in the work environment, and more data for making quick but balanced business decisions. Each individual business case can, of course, reap its unique benefits from edge computing, as living at the edge requires different things from different companies.
Rate this article
5/5.0
based on 1,108 reviews






