Benefits of remote patient monitoring and use cases for healthcare providers
Ensuring connectivity between various parts of the healthcare system is a rising trend. Bring the patient closer to the doctor, the symptom closer to the diagnosis, the diagnosis closer to the clinical decision, and, therefore, provide precise and efficient patient care faster.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is vital for achieving this connectivity. In this article, we take a look at how cutting-edge technological solutions can make the healthcare system more cohesive.
WANT TO KNOW HOW TO BUILD A SECURE AND EFFICIENT RPM APPLICATION?
Reach out to Yalantis and learn more about critical development aspects to consider and our experience delivering IoT-based healthcare solutions
Get more infoA brief look into what RPM is: Definition, benefits of RPM, and milestones
REMOTE PATIENT MONITORING (RPM) is a healthcare technology that allows medical professionals to track a patient’s health data outside of traditional healthcare organizations. This can take place in a patient’s home, a remote area, or anywhere with an internet connection.
Remote patient monitoring use cases:
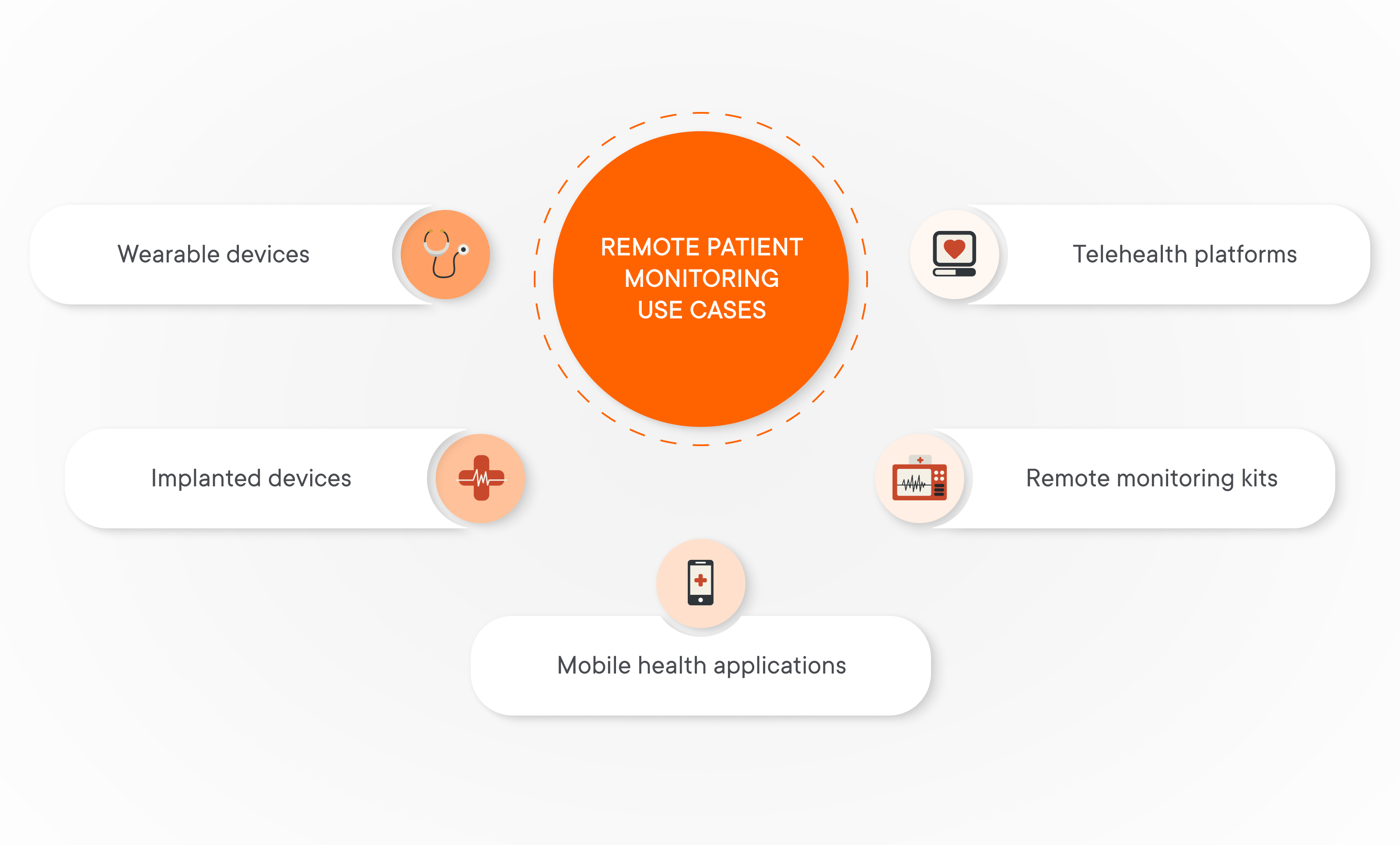
- Wearable devices (such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, ECG monitors). Wearable devices can track vital signs (for example, patient’s blood pressure monitoring) and provide real-time data to healthcare providers.
- Implanted devices (such as cardiac monitors or glucose sensors for continuous glucose monitoring). Implanted devices can continuously monitor internal physiological conditions, for example, glucose levels in diabetic patients or heart rhythm in patients with arrhythmias. Such monitoring sessions are crucial for patients who need constant monitoring and timely intervention.
- Mobile health applications. These apps allow patients to log their health data, receive medication reminders, and communicate with healthcare providers.
- Remote monitoring kits (blood pressure cuffs, pulse oximeters, weight scales). Remote monitoring kits include various tools that patients can use at home to measure their health metrics. They are used for patients with conditions like hypertension, heart failure, and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
- Telehealth platforms. Telehealth platforms with video conferencing functionality can facilitate remote consultations, diagnostics, and follow-up patient care. They are particularly useful for follow-up visits, mental health services, and initial consultations that don’t require a hospital visit and physical examinations.
How does PRM work?
Stage 1: Remote patient monitoring uses various digital tools to collect health information that includes vitals like:
- Vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation)
- Weight (monitored through smart scales)
- Blood sugar levels (measured with glucometers)
- Activity levels (steps taken, calories burnt, and overall activity time tracked by wearables)
Stage 2: This information is then securely transmitted to a healthcare provider’s platform (for example, EHRs), allowing them to monitor a patient’s condition remotely.
It’s obvious that such technology brings enormous potential to the healthcare field, enabling both patients and providers to make informed decisions about patient treatments and taking a proactive stance in personal health monitoring.
Therefore, the key benefits of remote patient monitoring in healthcare include:

- INCREASED PATIENT CONVENIENCE. Remote patient monitoring eliminates the need for frequent in-person appointments, freeing up valuable time for both patients and providers. This is especially beneficial for patients in geographically remote areas or those with mobility limitations.
- IMPROVED PATIENT-PROVIDER COMMUNICATION. RPM platforms often facilitate two-way communication between patients and providers. Patients can easily send questions or report any concerns, leading to more timely interventions and a stronger sense of connection with their healthcare team.
- REDUCED RISK OF INFECTION. By minimizing unnecessary in-person visits, remote monitoring can help to protect patients, especially those with compromised immune systems, from exposure to contagious illnesses.
- ENHANCED MEDICATION ADHERENCE. Certain RPM systems can send medication reminders and track medication use, improving a patient’s adherence to their treatment plan.
- BETTER QUALITY OF LIFE. By allowing for closer monitoring and improved management of chronic conditions, remote monitoring can empower patients to live fuller and more active lives.
Everything looks great for patients, but why is remote patient monitoring important for businesses?
How remote patient monitoring benefits businesses:
The global RPM market size is poised to reach $207.5 billion by 2028. You know why? Because RPM implementation already demonstrates mindblowing results:
- a 50% reduction in 30-day hospital readmissions for patients with heart conditions in the Cardiac Solutions practice (Phoenix, Arizona)
- an NPS patient satisfaction score of +86 and around a 50% reduction in inpatient utilization in Mercy Virtual Care Center (St. Louis, Missouri)
- a 23% reduction in overall mortality across the four Health First hospitals through the collaboration with Philips (Central Florida)
All of these also means:
- Substantial cost savings
- Constantly increasing customer satisfaction rate (and profits from potential clients attracted by good reviews)
- Business scaling
Considering these real-life examples, a logical question arises: how deeply has this technology delved into our everyday lives?
Let’s take a look at how the RPM adoption has been going:
The development path of RPM through years
We can break the development period of the RPM technology into four key stages, namely:
Stage #1: Early seeds (1990s)
The idea of remote patient monitoring found its roots in the 1990s with the development of basic telemonitoring technologies, such as physiological monitoring systems, telemetry systems, and others. These early systems primarily focused on monitoring vital signs in critically ill patients within hospital settings.
Stage #2: Technological advancements (2000s)
The 2000s witnessed significant advancements in communication technologies like mobile networks and wearable devices. We saw the first mobile health (mHealth) applications whereas fitness trackers and smartwatches started gaining wide popularity among the population. These innovations opened doors for the development of more sophisticated RPM systems capable of collecting a wider range of health data remotely.
Stage #3: Policy and reimbursement support (2010s)
The 2010s saw a crucial shift with the introduction of policies and reimbursement codes from government agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) in the US. They provided financial incentives for healthcare providers to adopt RPM technologies.
Stage #4: Remote monitoring takes flight (2010s onwards)
With supportive policies in place and technological advancements accelerating, the use of RPM began to gain traction in the late 2010s. The COVID-19 pandemic further fueled its adoption as a safe and effective way to monitor patients remotely.
And this is where the most interesting things start. How significant the pandemic really was for the remote patient monitoring field?
COVID-19: The era of the huge shift in the RPM paradigm
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, remote patient monitoring was a growing trend in healthcare, but its widespread adoption was gradual. However, the unique challenges posed by the virus significantly accelerated the use of RPM technologies. Let’s explore how COVID-19 propelled RPM into the spotlight.
How the pandemic changed everything
Due to the COVID-19 crisis, benefits of remote patient monitoring and management have come to the fore of the medical industry. Creating distance between the patient and the doctor was extremely critical during the pandemic because it provided both safety and the possibility for medical professionals to monitor and help more people.
And remote patient monitoring programs successfully address this challenge, enabling the following changes and improvements in the traditional healthcare realm:
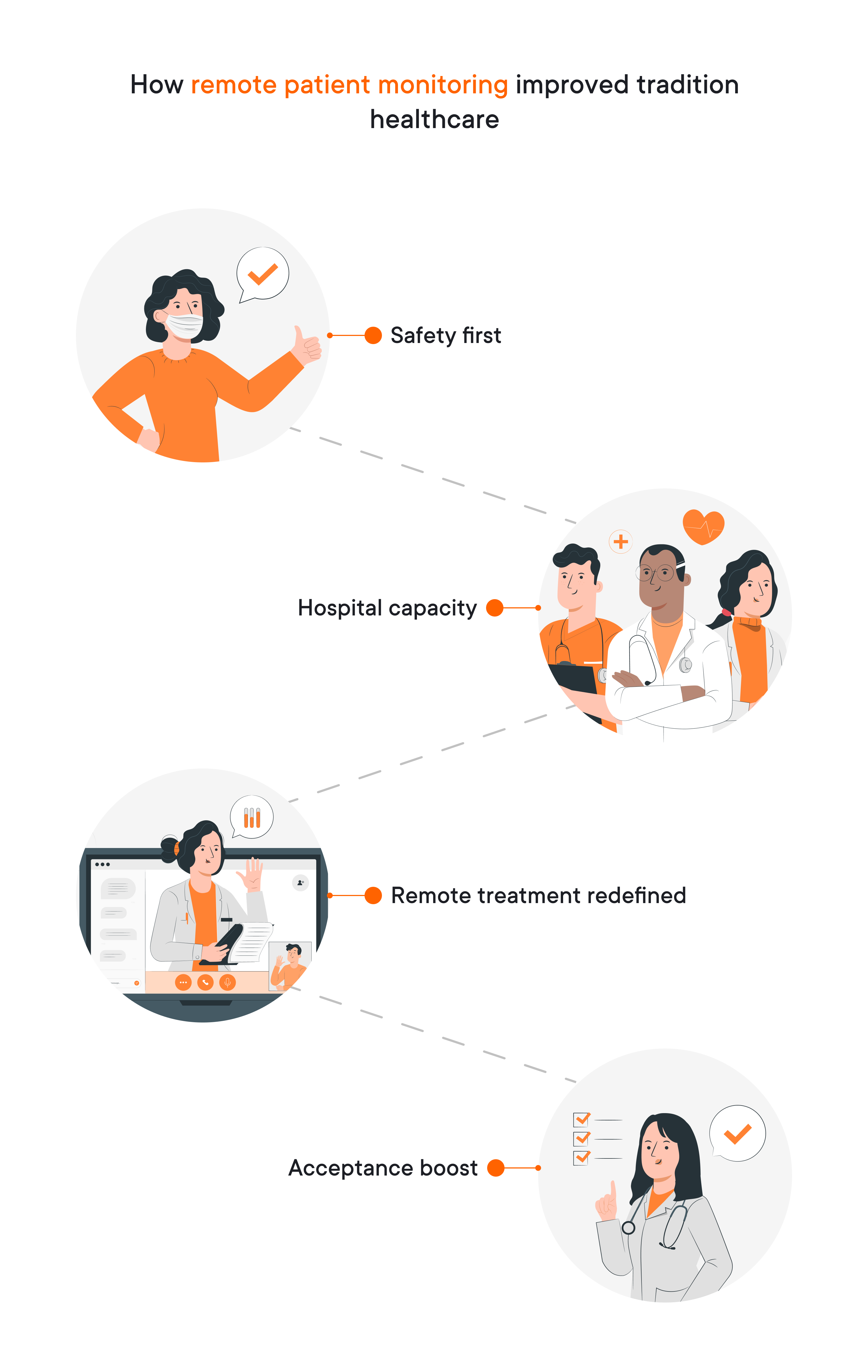
- Safety first. RPM programs offered a safe alternative, allowing healthcare professionals and primary care providers to track critical health data remotely, minimizing unnecessary in-person visits.
- Hospital capacity. The surge in COVID-19 cases overwhelmed healthcare systems, straining hospital capacity. RPM enabled the safe discharge of patients recovering at home, freeing up beds for critical cases. Additionally, RPM could monitor these recovering patients, allowing for early intervention if their condition worsened.
- Remote treatment redefined. The pandemic forced a rapid shift towards remote health care delivery. RPM, coupled with telemedicine consultations, became a powerful tool for doctors to diagnose, monitor, and even adjust treatment plans for patients remotely. Conditions previously requiring frequent in-person visits could now be managed effectively at home.
- Acceptance boost. Both patients and healthcare professionals became more comfortable with remote patient care due to the pandemic. Patients appreciated the convenience and safety of RPM, while healthcare providers saw its effectiveness in managing various conditions.
In circumstances when the number of medical specialists was limited as was the number of hospital beds for providing direct monitoring, the ability for a patient to send a distress signal and receive emergency aid was vital.
Considering all this, it’s no wonder that the remote patient monitoring device industry has been booming since then.
However, the peak is over. What can we observe now, after the COVID-19 climax?
Post-COVID remote patient monitoring examples and state: How far have we gone?
The COVID-19 pandemic wasn’t just a global health crisis – it also served as an unexpected accelerator for advancements in telemedicine. Initially used to manage COVID-positive patients remotely, reducing hospital strain and the risk of nosocomial infections, RPM has demonstrably improved healthcare delivery.
But the story doesn’t end there. As we move into the post-covid era, RPM is solidifying its place as a powerful tool, transforming healthcare in exciting new ways. Check them out:
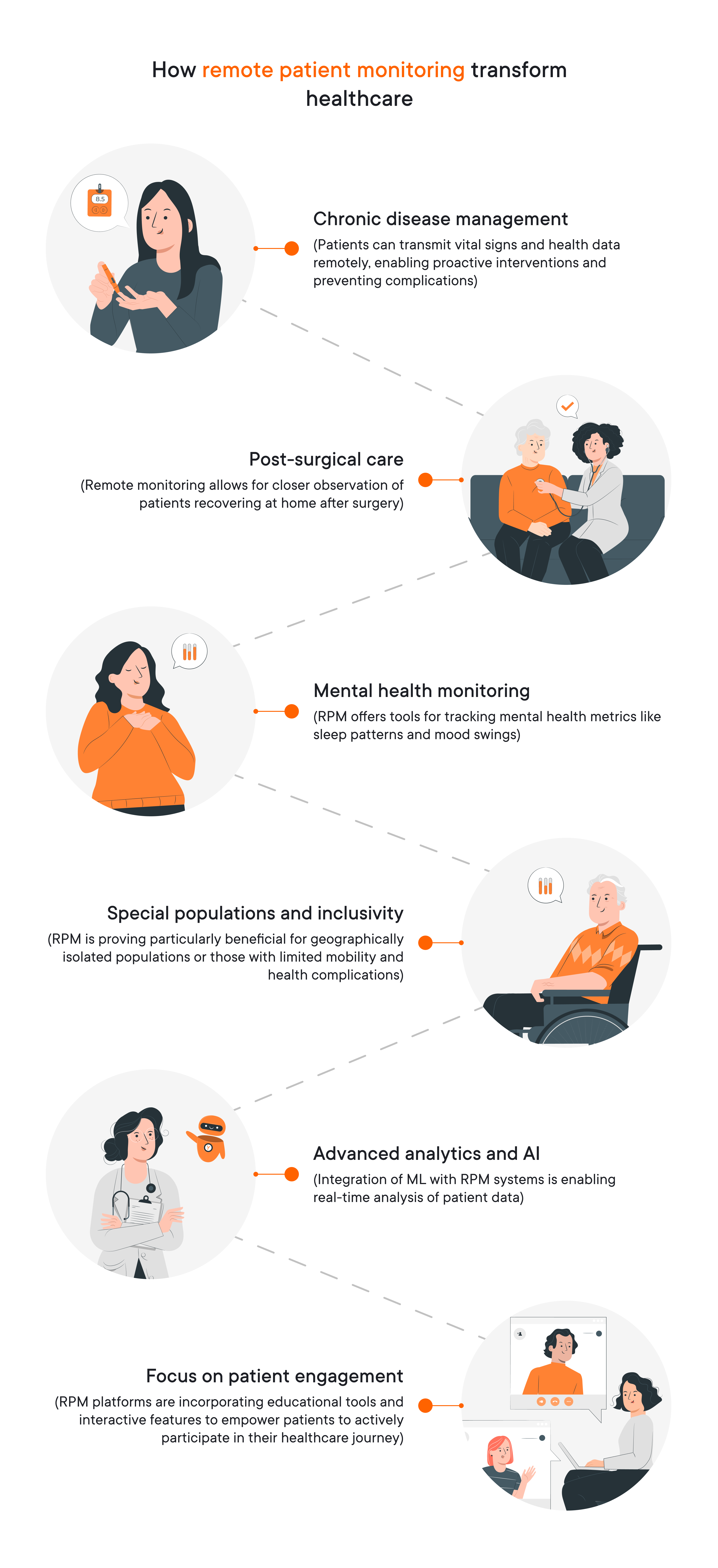
- Chronic disease management. RPM is proving invaluable in managing chronic conditions like diabetes, heart failure, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Patients can transmit vital signs and health data remotely, enabling proactive interventions and preventing complications.
- Post-surgical care. Remote monitoring allows for closer observation of patients recovering at home after surgery, reducing hospital readmission rates, improving recovery outcomes, and increasing the number of positive patient outcomes.
- Mental health monitoring. RPM offers tools for tracking mental health metrics like sleep patterns and mood swings. This data can be crucial for therapists and patients to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Special populations and inclusivity. RPM is proving particularly beneficial for geographically isolated populations or those with limited mobility and health complications. It empowers them to receive quality care without frequent in-person visits.
- Advanced analytics and AI. Integration of machine learning with RPM systems is enabling real-time analysis of patient data. Collaborating with a data science services company can help healthcare providers build robust analytics systems tailored to remote patient monitoring needs. This allows for identification of subtle changes that might indicate potential health issues, facilitating early intervention.
- Focus on patient engagement. The post-COVID phase emphasizes patient education and self-management. RPM platforms are incorporating educational tools and interactive features to empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey.
Despite the growing global acceptance of remote patient monitoring technologies, some health providers are still reluctant to implement them. This is mostly because of the hardships associated with implementation — namely, problems with authorization and unclear benefits of remote monitoring.
Let’s talk about how to ensure RPM implementation.
Key components of a remote patient monitoring system
RPM systems are mostly considered a kind of IoT network. However, remote patient monitoring is wider than IoT and includes some cases with direct human-to-device interaction.
Here are some key components of an RPM system:
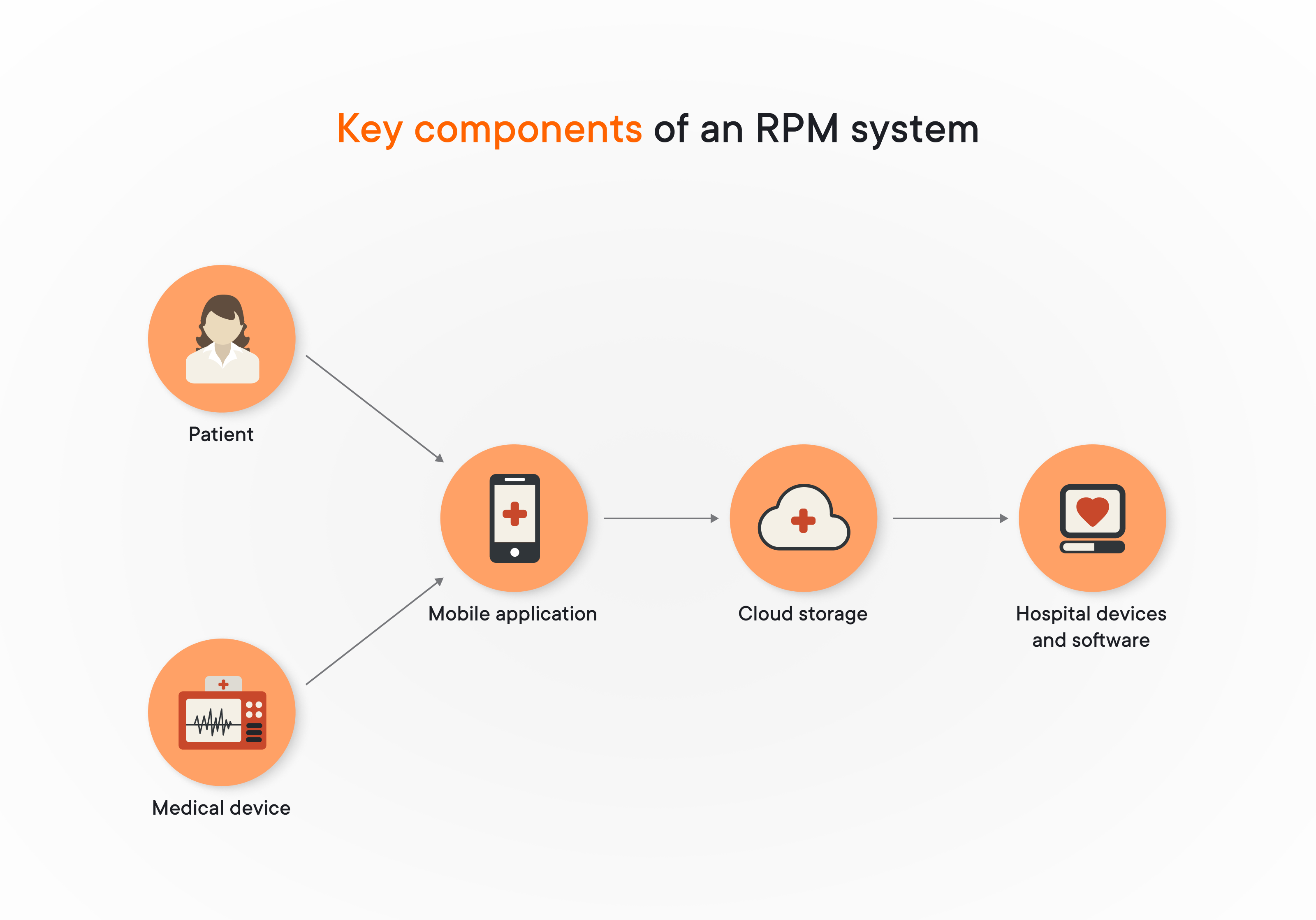
Let’s talk about RPM system components in detail and find out problems they help to solve in order to obtain the most accurate picture of a patient’s health condition.
#1: Medical devices collecting data about patient conditions
All medical tools and IoT medical devices provided by the modern medical industry deal directly with the subject of human health and well-being; therefore, they require careful scrutiny and thorough control.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) provides authorization for medical devices and decides whether they can be used as a source of data sufficient for clinical decision-making.
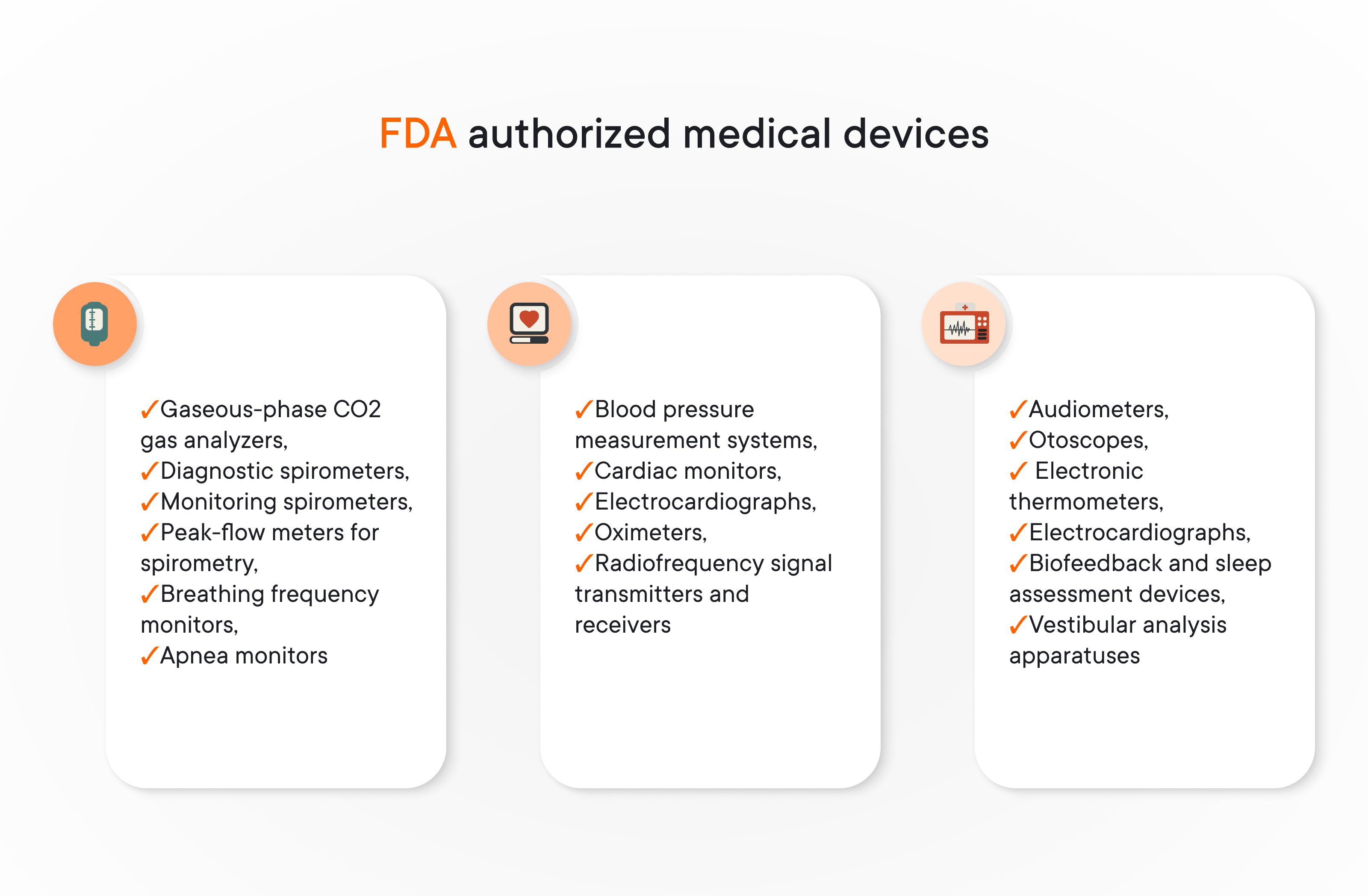
YALANTIS HELPED ONE OF OUR CLIENT OBTAIN AN FDA CLEARANCE FOR THEIR MEDICAL DEVICE
Learn moreHow does it work?
All patient-side RPM devices gather data and send it further — to the mobile device, such as a tablet or phone, and to a mobile application for patients. Several wireless technologies can be used to transmit data from an RPM medical device to a mobile application, but Bluetooth Low Energy is the most commonly used.
Although only data from authorized medical devices can be used for clinical decisions, medical specialists can also find data from common wearables (such as fitness trackers and smartwatches) useful. Yalantis even helped one of our clients integrate their patient-facing application with smartwatches for the broader context. The healthcare community is still discussing this matter, but the overall opinion towards common wearable devices is becoming increasingly positive.
Another way health data can be gathered is manually by the patient.
#2: A patient as a core information supplier
IoT is great, but devices cannot measure everything, at least for now. No sensor can detect a patient’s overall mood and how it changes over time, or detect a patient’s subjective level of depression. Still, these factors are really important in creating a broad picture of illness, especially when it comes to long-term diseases such as cancer.
How to solve this problem?
Such information can be obtained via a questionnaire or a feedback form filled out manually by the patient. After the data is filled in, it is then processed by a mobile application and sent to the cloud, where it can be analyzed by medical professionals.
Here are some of the parameters that patient-managed remote control applications can gather:
- Overall mood and feeling of wellness
- Sleep quality
- Whether a patient feels well-informed about the illness and possible treatment
- Level of accomplishment in daily activity
- Feelings of nausea
- Weight loss or gain
- Social activity
This list can be long and must be specific for each particular illness.
Analog data undergoes digital transformation and is sent to the next component: the patient-side mobile application.
#3: Mobile application as an intermediary between a patient and medical device
Mobile applications act as a bridge between patients, their medical devices, and the healthcare providers receiving the collected health data. However, these apps must navigate a tricky path. On one hand, they need to comply with a variety of regulations to ensure patient privacy and data security. On the other hand, they must also be user-friendly to encourage patient engagement and maximize the amount of valuable health information collected.
Achieving this balance is key. The app’s security features should be robust without becoming overly complex and frustrating for patients. Transparency is also crucial: patients need to understand exactly what data is being collected and how it’s used. A well-designed user interface that is easy to navigate and accessible for users with disabilities is essential for maximizing patient adoption.
#4: Cloud data storage where all data is kept and distributed
Cloud storage in remote patient monitoring acts as a central hub for collected health data. This data can arrive in two ways:
- Mobile app gateway
Most commonly, information is transmitted from the patient’s mobile application, which acts as an intermediary between the medical device and the cloud storage.
- Direct device connection (less common)
In some rare cases, if the medical device itself has strong enough connectivity features, it might transmit data directly to the cloud storage, bypassing the mobile app.
Once the data reaches the cloud, it’s then securely transferred to the healthcare provider’s systems for analysis and monitoring. This centralized storage allows healthcare professionals to access patient information from various remote patient monitoring devices and locations, facilitating comprehensive care management.
#5: Hospital devices and software that analyze info about patient health
This is another part of the RPM flow where an application is needed, often being integrated with a general EHR system.
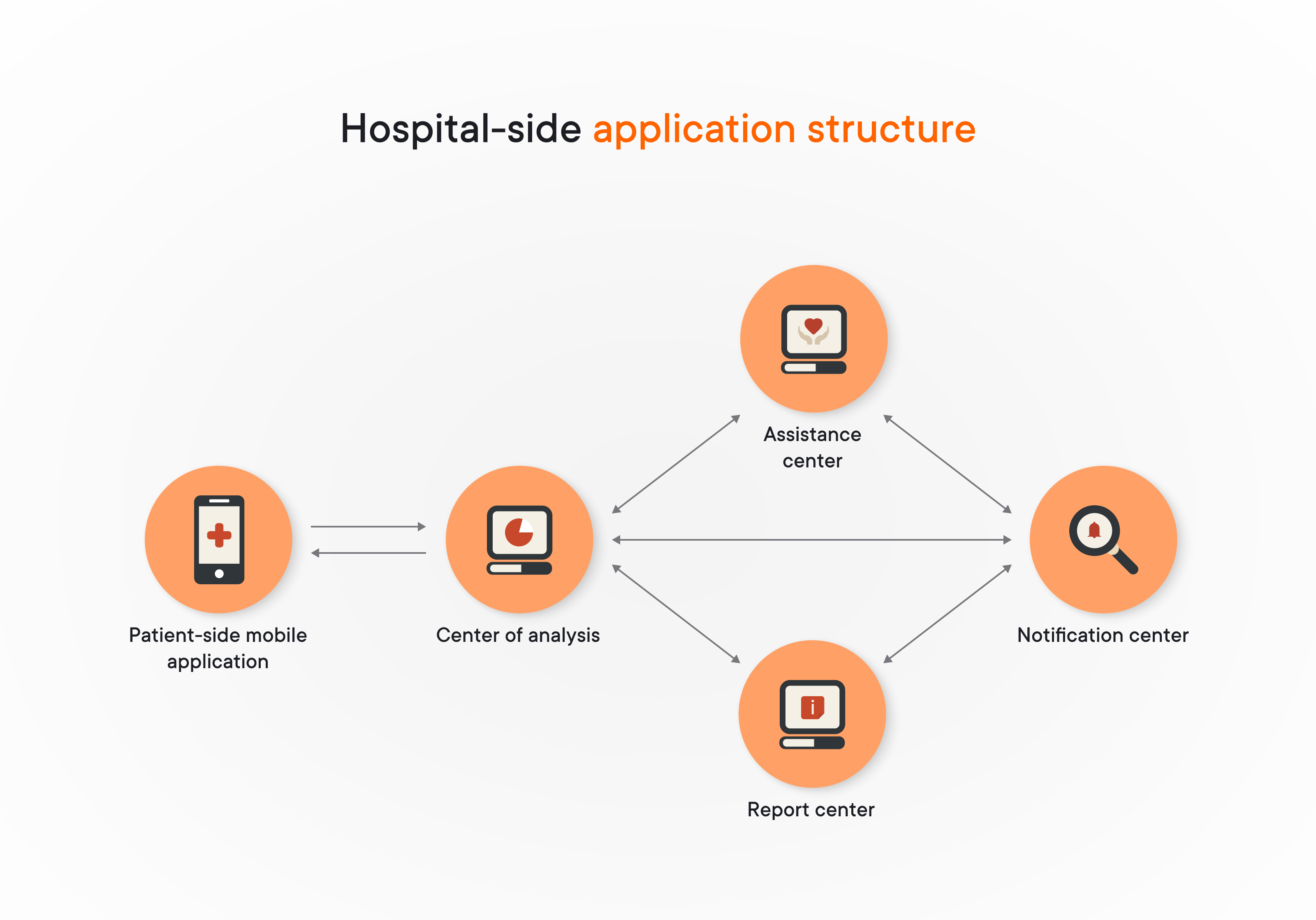
On the hospital side, the application should consist of several main centers, each with its own function:
- The center of analysis provides medical personnel with complete and processed patient generated data along with visualization tools and business intelligence. It is the main part of the application that allows doctors to make informed clinical decisions.
- The assistance center is a tool that automatically compares data received from the patient to the limits set by the doctor. If the limits are surpassed, this information is transmitted to the notifications center.
- The notifications center part of the application is designed to generate warning messages once the assistance center discovers that limits have been surpassed. If they are, a notification is immediately sent to the medical specialist responsible for monitoring.
- The report center gathers all information generated by measurements and their processing, arranges them into reports, and sends them to the person responsible.
What’s next?
After data has been received and processed on the hospital side, the next step is for hospital staff to react. The responsible healthcare professional either makes a clinical decision on changes in the treatment process or, if the information was obtained by unauthorized devices such as fitness trackers, gives general recommendations to the patient.
RPM systems are generally very useful, but they excel in telehealth solutions. A large portion of healthcare institutions have already implemented telehealth solutions into their workflow, and they can be improved by adding RPM functionality.
Examples of remote patient monitoring application development approaches: How to put together a puzzle of essential components
Custom software development for an RPM system can be divided into two main parts:
- building the patient-side application
- building the hospital-side application
Patient-side application
First of all, a patient’s interactions with the RPM solution have to be as clear as possible: the effectiveness of data gathering depends on it, as does the overall quality of treatment by extension. It is also important to consider that the application’s UI/UX must be accessible for various user groups, including elderly people and people with motion and/or vision limitations.
Besides, an application intended for a patient’s mobile device has to meet a certain set of criteria:
- Support the correct protocol for interaction with IoT medical devices gathering vital patient data. Most likely, these devices would use the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) protocol, but they may also use LoRaWAN or other standards.
- Maintain a high level of security for protected health information and comply with HIPAA regulations
- Be able to integrate into a system of interconnected medical software products by establishing a connection with the hospital-side system through a secure API that supports HL7 FHIR standards
- Caching mechanisms to prevent connectivity issues in case of network failures
In addition to meeting these criteria, you could implement a great number of upgrades and improvements according to your particular requirements.
An example project from Yalantis’ experience: How we redefined an existing telehealth solution
The Yalantis team needed to enhance the functionality of both patient-side and hospital-side applications considering the benefits of remote patient monitoring. The client’s focus was on integrating IoT elements into their telehealth solution (IoT solution) and increasing the effectiveness of overall patient treatment. Here are the improvements we introduced into the patient-side application:
- Improvements aimed at the patient experience. The user interface was lacking in terms of user-friendliness. We created a new UI, making it easy for patients to navigate, send information, follow guidelines from medical professionals, track overall treatment progress, and give feedback. We also made sure that the UI was clear and understandable for all age groups and patients in any physical condition.
- Live visit mode with vitals tracking. We added a feature that allows the application to automatically detect when an online doctor visit is live and switch to a mode that allows the doctor and patient to seamlessly interact with each other and share real-time medical data.
- Comprehensive patient dashboard. A patient’s understanding of the treatment flow and their state is crucial for overall treatment success. Therefore, we implemented an overview with all data accumulated over a certain period presented in a clear and easy-to-read form.
- Doctor-controlled schedules. Another effective tool for maintaining the treatment flow is a scheduling system. It’s a great way for doctors to assign times when patients should do any kind of routine activity: take medication, check vital signs, or perform physical exercises. The system sends automated notifications to patients.
Hospital-side application
The hospital-side application has its own set of requirements to comply with, including:
- HIPAA requirements. Just like with the patient-side application, HIPAA compliance must be maintained at all times.
- Healthcare interoperability standards. The application must be able to successfully become part of a complex device and software system, which most of the time means adopting HL7 FHIR and US Core Data for Interoperability (USCDI) standards.
Because RPM involves sensitive patient health data, adhering to compliance regulations is paramount, here’s why:
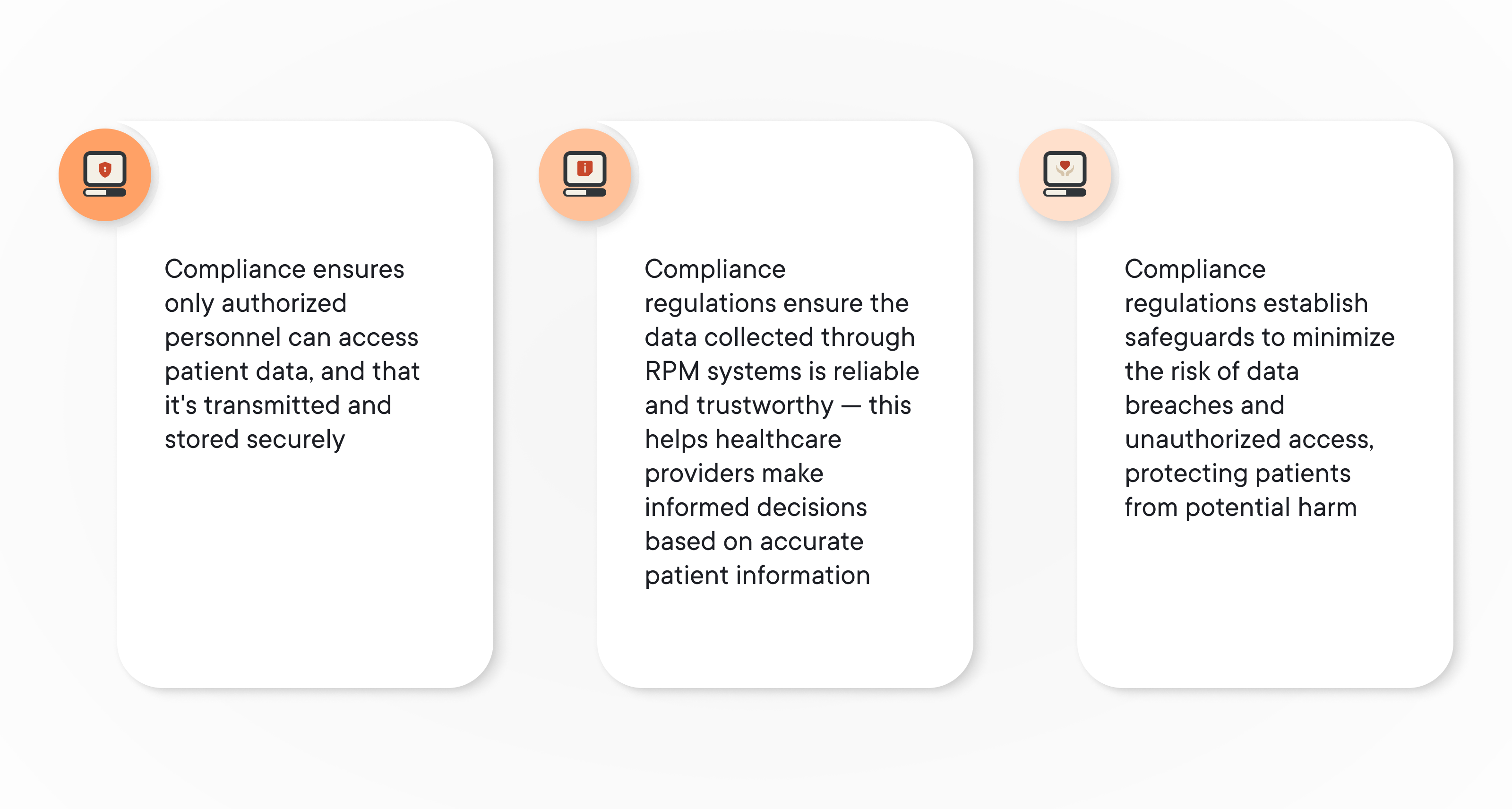
Part 2 of an example project from Yalantis’ experience: What we did for the hospital-side application
Getting back to the Yalantis IoT integration case we described above, we also made some major improvements to the existing hospital-side application. Here are some of the most important enhancements we did using all benefits of remote patient monitoring:
- Notification system. The system constantly receives data from vital sign sensors and sends out notifications as soon as changes reach a pre-established threshold indicating a serious deterioration in the patient’s state. Medical professionals monitoring the system can then react accordingly, administering urgent measures.
- Synchronization of online sessions with tracking process. The second half of the synchronization system is built into the hospital-side application. The doctor can review measurements taken during the online visit and analyze them without interrupting the visit.
- Enhanced monitoring and control of vitals data. We made the visual representation of information gathered from vital sign sensors more user-friendly and easier to handle. A plethora of visual tools are now available to the user, such as graphs and tables, so that even large amounts of information can be processed by the doctor.
- Routine creation tool. Now doctors can create customized routines for patients, setting times for medication intake, physical exercises, vital sign checks, and online visits. Notifications are sent to patients, ensuring their awareness and improving the treatment flow.
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR EXPERIENCE REDEFINING A HEALTHCARE SOLUTION
Read case studySetting up your IoT remote patient monitoring system is a great way to ensure a constant increase in healthcare service quality, but it’s not the limit. Yalantis specialists can assist you in building another kind of RPM: a Patient-Reported Online Measures (PROM) system (IoT app development services).
Beyond IoT: PROM remote patient monitoring apps
Despite the plethora of benefits of remote patient monitoring, Some medically significant metrics cannot be measured via IoT devices alone. Especially in the case of chronic and long-term diseases such as cancer or diabetes, many things crucial for the treatment process can only be measured or assessed by patients themselves.
Therefore, patient-reported outcome measures, or PROMs, keep gaining importance in the field of medical data assessment. Of course, the subjective experience of the patient cannot (for the most part) be a reason for a clinical decision. However, it can be used for creating a general picture of treatment progress and as a basis for recommendations aimed at improving a patient’s quality of life. PROM-based applications can also include access to online patient portals, creating self-help groups, and providing a sense of unity.
Here are some important points on the importance of PROM applications:
- Patient reported information helps medical professionals establish the most effective treatment practices by presenting large amounts of data on the pain levels, physical function, and mental state of patients, simultaneously aiding in making clinical decisions.
- PROM questionnaires can use both generally accepted standards — such as SF-36, VAS, or EQ-5D — and implement more specific sequences developed for a particular ailment.
- PROM questionnaires should be created with user-friendliness and compactness in mind; an abundance of information can lead to patients getting bored and annoyed and can therefore reduce patient compliance.
- PROM systems are also useful for creating predictive models. Establishing patterns in patients’ states and treatment flows makes it easier for doctors to make clinical decisions and leads to more cost-effective services.
Our specialists believe that the trend toward PROM systems and applications will continue to grow, especially as more and more healthcare providers switch to value-based services.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the rules in the healthcare industry forever. No matter how long it takes to overcome the coronavirus, the changes are here to stay as well as the benefits of remote patient monitoring.
People will rely more and more on remote healthcare IT, be wary of face-to-face interactions, and expect the industry to be ready for the next global pandemic. The best way for healthcare providers to demonstrate such readiness is to employ reliable remote healthcare technologies now.
RPM systems, however, are more than an alternative to on-site healthcare. They intertwine with it and expand its limits. They can allow patients to register a lot more data on their health and general state of body and mind, leading to an increase in the effectiveness of in-person visits to the doctor.
RPM systems are gathering data in much larger volumes than traditional medical methods, and they are also teaching patients to be more attentive towards their health, which underlines the great benefits of remote patient monitoring.
YALANTIS HAS SPECIALISTS WITH IMMENSE EXPERTISE IN REMOTE PATIENT MONITORING
If you want a reliable partner or an expert consultation on such matters, contact us — we would be happy to help
FAQ
What’s remote patient monitoring?
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) involves using digital technology to collect and transmit patient generated data from patients to healthcare providers in real-time, which, in turn, allows for continuous monitoring and management of patient medical conditions outside traditional clinical settings.
What are the benefits of remote patient monitoring?
The benefits of RPM include:
- an increased number of positive patient outcomes
- enhanced convenience for patients
- early detection of potential health issues and better treatment of chronic diseases
- reduced hospital readmissions and hospital visits
- cost savings for patients
- an increased number of treated patients for healthcare professionals
What are the examples of remote patient monitoring?
Examples of RPM include wearable devices that track vital signs, glucose monitors for diabetes management, home-based blood pressure monitors, and telehealth platforms that facilitate virtual consultations and follow-ups.
Rate this article
4.2/5.0
based on 27 reviews