Wearable devices, as we know them, appeared on the market in the early 2000s, and later in the decade, all tech giants presented some sort of wearable technology: Apple SmartWatch, Google FitBit, Garmin Forerunner — you name it, and they probably have it.
These days, most wearables track things like heart rate, sleep, and daily activity. Specialists can use data obtained from wearable devices as a supplemental technology for remote patient monitoring (RPM), early disease detection, and creating tailored treatment plans, which could reduce the number of hospitalizations.
However, the true potential of adopting wearables for healthcare spans beyond that. In this article, we’ll discuss how healthcare wearable app development and adoption can potentially become a stepping stone on the pathway to making healthcare available to everyone. Yalantis wearable app developers will also offer you guidance on how to create an app that will be appreciated by healthcare providers and patients alike. So be sure to read on to grab some insights!
Interested in medical software development services?
We engineer Class II/III medical devices from hardware and software to certification, proven to cut post-market costs by 30%.
State of wearable application development market and potential growth directions
Since its emergence, the wearable application market has been experiencing steady growth from $10.6 billion revenue in 2019 to an estimated $67.2 billion revenue by 2030. During this period of growth, wearable apps will continue to generate the most revenue.
Based on the same GlobeNewsWire report, the highest CAGR — 18.8% — is expected in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, specifically in China and India. Several factors contribute to this, mainly tech advancements in the region that allow the production of cheaper devices, average income increase, and the general population aging, which means that more people will want to keep tabs on their health.
Speaking of other regions, North America continues holding the largest market share, 33.8%, followed by APAC and Europe. Americans prefer using smart devices and wearable apps to monitor daily steps, calorie expenditure, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
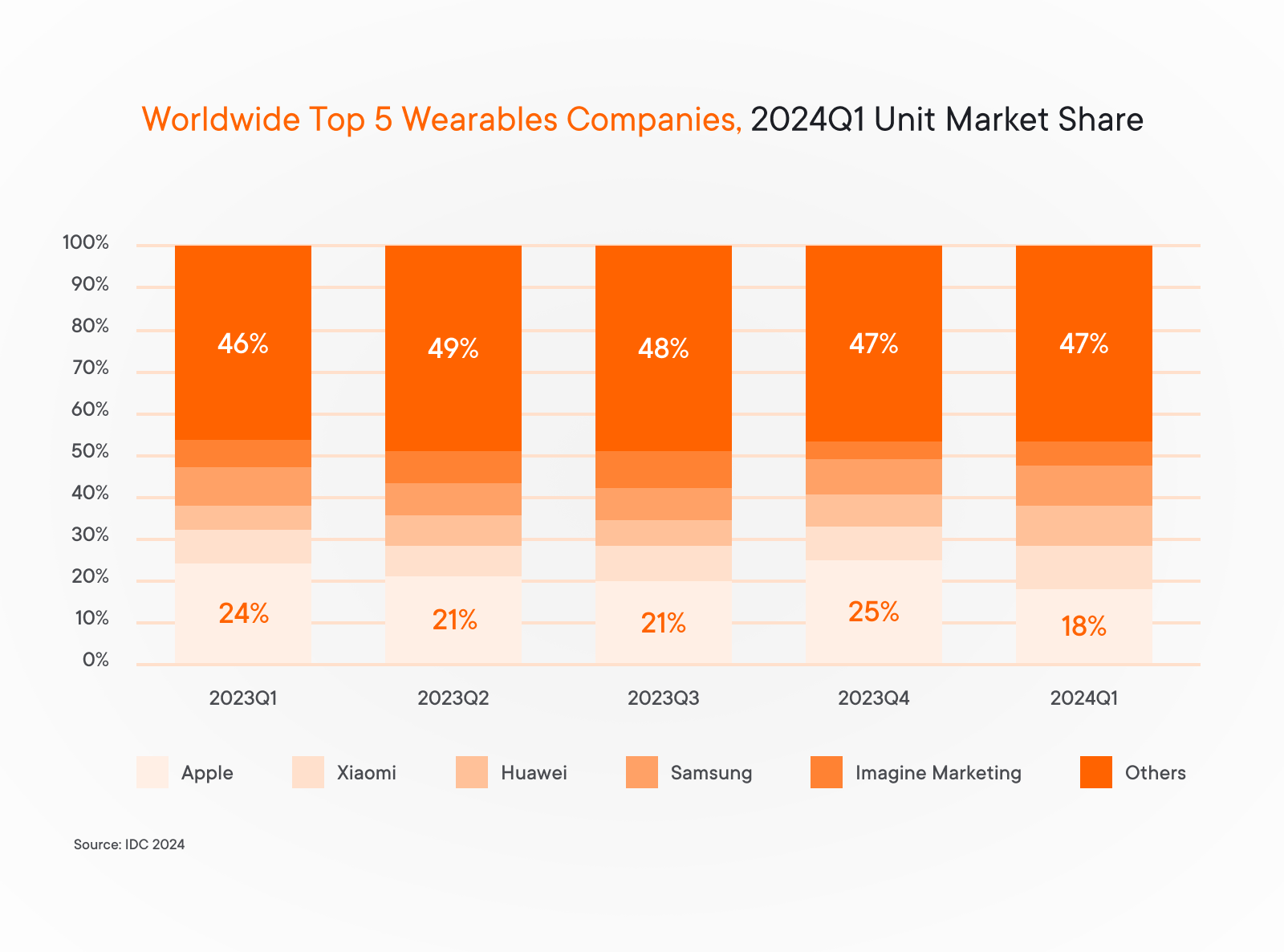
Another marker signaling that the companies are aiming to invest in wearable apps development and make them more available for the general public is the 11% drop in average selling price in Q1 2024 for five major wearable technology developers: Apple, Xiaomi, Huawei, Samsung, and the Indian wearable manufacturer, Imagine Marketing.
Finally, let’s look at the wearables ownership statistics by age. A 2023 report by Datareporter states that the highest wearable ownership rates are among the adults between 25 and 34 years — 27.2% among females and 26.9% among males. Older people (55+) are still somewhat reluctant to adopt user friendly wearable apps, even though some of them understand that it can improve their autonomy and subjective well-being in the long-run.
Based on these findings, we can say that main drivers of wearable device market growth are:
- Growing need for remote patient monitoring. Global population aging and increasing share of chronic diseases affect the demand for RPM. Wearable devices offer continuous health monitoring, allowing patients to stay informed about their health conditions.
- Focus on preventative care. Wearable mobile apps play a significant role in helping healthcare providers monitor the health of patients with chronic diseases. They allow them to detect anomalies on time, adjust or change the treatment, and reduce hospital visits thanks to real-time health tracking.
- Increasing awareness about health. General public today has a higher level of awareness about their health thanks to wellness and fitness influencers, which prompts them to adopt a wearable app for health monitoring.
- Technological advancements. Constant breakthroughs in software development among the tech giants, the rise of the global mobile market, and increase in wearable app developers demand drive the adoption rates for wearable devices.
But where there are drivers, there are also pitfalls. Let’s explore what factors hinder the medical wearable development and adoption of a wearable app and how we can address them.
Challenges that prevent healthcare facilities from leaning into wearables app development and how to solve them
Even though the wearable devices application development segment is on the rise, there’s still lots of work ahead, particularly in the healthcare field. Here are some of the main challenges encountered by businesses trying to integrate wearable app development services with healthcare systems.
Integration complexity for hospital systems
The first set of challenges arises when it comes to integration of a wearable app with existing hospital information systems (HIS) and electronic health records (EHR). Main reasons for this are:
- the overall complexity of hospital legacy systems
- lots of differing data formats
- multiple sensors and various communication protocols for medical equipment
- system interoperability issues.
Recommendations from Yalantis experts:
- Use standard protocols, such as HL7 and FHIR standards for seamless data exchange.
- Invest time and resources in API development, creating robust APIs to facilitate integration with various hospital systems.
- Implement middleware solutions to bridge gaps between wearable devices and hospital systems.
- Increase collaboration between IT teams and hospital IT departments to ensure compatibility and smooth integration.
These steps can simplify software development and integration processes, ensuring efficient and accurate data flow between wearables and hospital systems.
Consumer concerns about data protection
Wearables monitor and collect data such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels in the companion app. Some of them also have functionality like in app purchases, social user interaction features that include geolocation. This information is often stored in the cloud, and it’s unclear who has access to it and how the data is being used.
Recommendations from Yalantis experts:
- Make sure that your data storage and protection policies are clear and easy to understand.
- Explicitly explain to users how, where, and how long the data is stored, how it’s used, and how the customers can minimize data exposure, for example, by setting up two-factor authentication in the app.
Lack of understanding of the benefits of wearable products among healthcare providers
Healthcare providers often struggle to adopt wearable technology due to a lack of understanding of its potential benefits, such as real-time health monitoring and early disease detection, which can significantly enhance patient care and outcomes.
Recommendations from Yalantis experts: to bridge this gap and make healthcare providers more accepting towards your IoT based wearable apps, conduct educational workshops and demonstrate successful case studies that highlight the role of wearable applications development in patient monitoring. Focus on clear, evidence-based information on how wearable apps can improve patient management, reduce hospital readmissions, remove the excessive load from medical staff, and enhance overall healthcare efficiency.
Regulatory and compliance complications
If you invest into medical device app development, you must be sure that your IoT solution adheres to multiple laws and regulations, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and others. In the US, wearable apps must also receive approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that confirms their efficiency and safety for daily use.
Recommendations from Yalantis experts: make sure you evaluate the application and see if it meets the mandatory compliance requirements. We have a comprehensive HIPAA checklist for everyone who develops medical software, so you can start from here.
Also, it’s a good practice to have a compliance specialist on board. They will help you navigate the intricacies of wearable application development process in regard to international laws and regulations, and prevent negative consequences of being non-compliant, such as fines, money loss, or inability to launch your product in certain markets.
Concerns about the measurements accuracy
Unlike blood glucose monitors, blood pressure monitors, cardiac sensors, and other tech that is used in clinical settings, the efficiency of modern Wear OS apps or Apple Watch apps isn’t backed up by science as good.
Recommendations from Yalantis experts: This is the wearable app development challenge that business itself cannot properly solve without detailed market research and population studies backed by science. However, you can provide clear wearable app instructions for users and explain the development process and technologies behind health monitoring in a way that would make skeptics change their minds.
Computational limitations of wearable devices
You physically can’t fit a lot of precise tech into a small wearable app, which creates constraints for wearable apps development, particularly in terms of device memory usage and ability to process complex data and tasks.
Recommendations from Yalantis experts: There are a lot of strategies that help address technical limitations. Here are some strategies that Yalantis, as a wearable app development company, has found out to be successful:
- Optimizing software: Develop lightweight, efficient wearable applications that minimize resource usage.
- Introducing edge computing: Process data locally on mobile devices to reduce the load on central servers.
- Integrating apps into cloud: Offload intensive computations from existing mobile application to the cloud, ensuring seamless performance.
- Updating software regularly: Provide software updates to enhance performance and security.
Non-intuitive features of wearable devices
Finally, some users, especially among older populations, might have a longer learning curve when it comes to adopting wearable applications for daily use. This is often due to complex device settings, non-intuitive user interface, or design that’s non accessible to users with physical or cognitive impairments.
Yalantis, a wearable app development company, recommends these tips to avoid common design problems:
- Implement accessibility guidelines into a device’s UI. You can refer to Google’s Accessibility Guide for Wear OS, Apple’s Watch OS Design Guide, or other similar resources. Focus on clear icons, text, and navigation to additionally reduce complexity.
- Incorporate voice commands. Implement voice-activated controls to make mobile application easier to understand, especially for those who may struggle with touch interfaces.
- Provide comprehensive training. Offer easy-to-understand user guides, video tutorials, and in-person training sessions. Support users with step-by-step instructions to ease the learning curve.
Now, let’s talk about how wearable applications can drive forward patient-centric care and, in the long run, make health more available for everyone.
Compliance mistakes cost more than you think
Cut rework and service costs before they happen with our free ISO 13485 + FDA compliance guide.
How will wearable device app development and integration of wearables with hospital systems benefit patient care?

It’s a known fact that the healthcare industry slowly accepts any change. However, wearable app programming and adoption could become a potential stone that triggers the transition to more patient-centric care.
Overall benefits of wearable devices
- Continuous health monitoring. Wearable app enables 24/7 tracking of vital signs and physical activities, providing real-time health data that can lead to early detection of medical conditions and prompt interventions.
- Personalized healthcare. By collecting detailed personal health data, a wearable app facilitates tailored treatment plans and lifestyle recommendations, improving patient outcomes and adherence to medical advice.
- Enhanced patient engagement. Wearable technology encourages patients to actively participate in their own healthcare by providing insights into their health metrics, fostering better self-management and awareness.
- Remote patient monitoring. Apple Watch and Wear OS wearables allow healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely, reducing the need for frequent in-person visits and enabling continuous and high-quality care for chronic disease management.
- Improved emergency response. Many wearable applications come with features such as fall detection and emergency alerts, ensuring that immediate assistance is provided in critical situations, thereby enhancing patient safety.
- Data-driven insights. The extensive data collected by wearables such as smart rings can be analyzed to identify health trends and patterns, assisting in preventive healthcare and informing clinical decisions for better treatment strategies.
Use cases for wearable devices in various medical fields
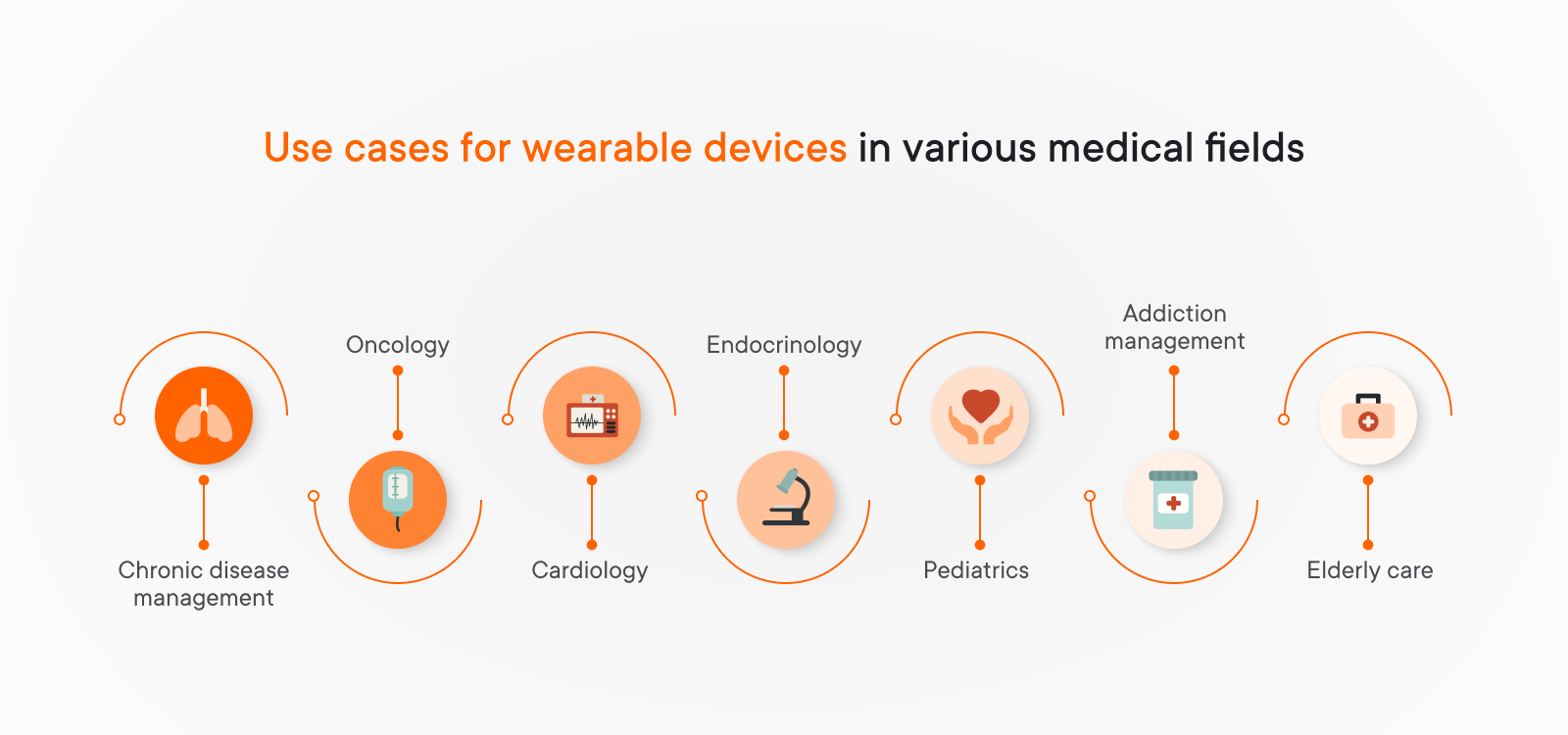
- Chronic disease management. Thanks to real-time data tracking, wearable applications can be used by healthcare providers to monitor patients with chronic diseases, prevent flares, and promptly correct treatment plans.
- Oncology. Wearable app development in oncology creates products that can monitor vital signs and detect early signs of complications such as infections or heart issues in patients undergoing chemotherapy, improving timely interventions and overall patient management.
- Cardiology. In cardiology, a wearable app or a smart clothing can continuously track heart rate, rhythm, and blood pressure, allowing for early detection of arrhythmias or hypertension, and enabling remote patient monitoring for individuals with chronic heart conditions.
- Endocrinology. Wearable glucose monitors in endocrinology provide real-time blood sugar levels for diabetes patients, helping them manage their condition more effectively by adjusting insulin doses based on continuous data.
- Pediatrics. Apple Watch and Wear OS devices for children can track activity levels, sleep patterns, and vital signs, assisting in the early diagnosis of conditions such as sleep apnea or asthma, and ensuring comprehensive health monitoring.
- Addiction management. A wearable app can support addiction treatment by tracking physiological signs of stress and cravings, providing real-time feedback and alerts to both patients and caregivers, and integrating with apps for behavior tracking and intervention support.
- Elderly care. In elderly care, a wearable app will monitor vital signs, physical activity, and fall detection, enabling real-time alerts for caregivers and emergency services, thus ensuring prompt assistance and enhancing safety and independence for seniors.
How wearable tech can help to reduce health disparities?
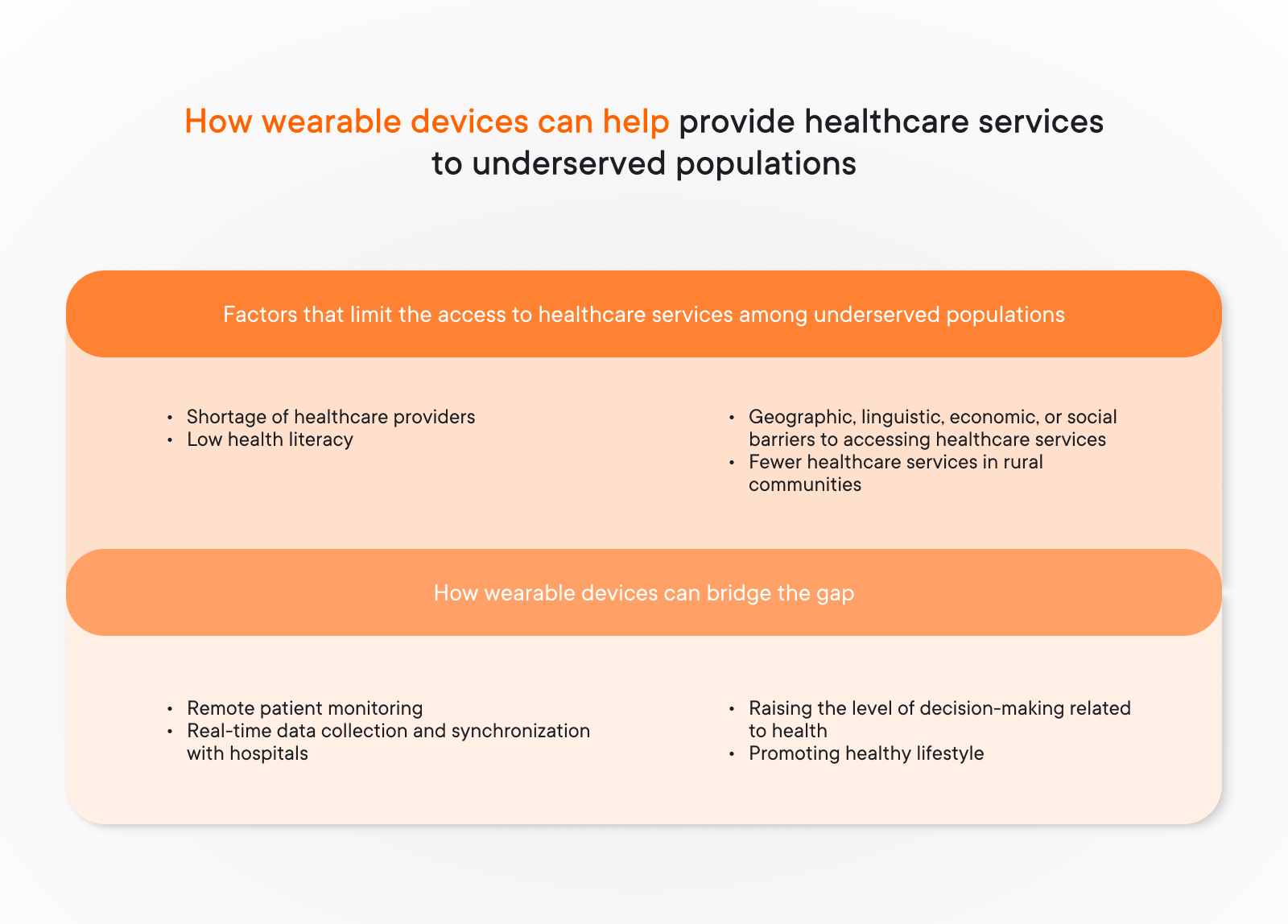
Wearable technology can significantly reduce health disparities by providing accessible and affordable health monitoring and care. For instance:
- For underserved populations, wearable app offers a cost-effective means to track vital signs, manage chronic conditions, and receive timely health interventions without needing frequent visits to healthcare facilities.
- Remote monitoring through medical wearable IoT development and integration ensures continuous healthcare access, particularly benefiting rural or economically disadvantaged areas with limited medical services. These devices can bridge gaps in healthcare by delivering real-time data to healthcare providers, enabling prompt responses to health issues and reducing the risk of complications.
- Wearable technology empowers individuals with personalized health insights, encouraging proactive management of their health and promoting healthier lifestyles. By democratizing access to health information and care, app development for wearable devices contributes to reducing the disparities caused by socioeconomic factors, geographic isolation, and lack of healthcare resources.
Overall, wearable technology can enhance healthcare equity by making health monitoring and management more accessible, affordable, and effective for all populations, particularly those who are traditionally underserved.
WANT TO KNOW HOW TO BUILD A WEARABLE ARECEIVE A DETAILED CHECKLIST FOR BUILDING A WEARABLE APP THAT YOUR CLIENTS WILL LOVEPP THAT WILL BE LOVED BY PATIENTS AND HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS?
Get the checklistHow wearable devices app development can further transform hospital systems to help them offer better care?
Improving patient engagement and offering treatment plans based on real-time data collection is much closer now than we’ve dreamt a few years ago. To make the most of patient data and actually improve their outcomes, healthcare facilities need to adopt multi-domain approach to patient care, which includes wearable app development in synergy with multiple modern technologies:
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI can significantly enhance hospital systems by automating routine tasks, reducing human error, and providing predictive insights. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data collected from Apple Watch or Wear OS to predict disease outbreaks, personalize treatment plans, and identify patients at risk of complications.
- Augmented reality (AR) and Virtual reality (VR): Augmented reality can be used in surgeries to provide real-time, 3D visualizations of patient anatomy, assisting surgeons in complex procedures. VR can offer immersive training simulations for medical professionals, enhancing their skills without the risks associated with real-life practice. Additionally, VR can be used for pain management and rehabilitation, providing patients with therapeutic environments.
- Data analytics: Data analytics uses historical data to forecast future outcomes. In hospitals, it can predict patient admission rates, optimizing resource allocation and reducing wait times. It can also anticipate patient deterioration, enabling timely interventions.
- Data visualization: Effective data visualization tools transform complex data sets into intuitive, actionable insights. Hospitals can use dashboards to monitor key performance indicators, track patient outcomes, and identify trends. Data visualization aids in decision-making by presenting data in a clear, understandable format, facilitating better communication among healthcare teams.
By integrating these technologies, hospital systems can become more efficient, accurate, and patient-centric. These advancements not only enable users to engage in decisions about their health but also optimize hospital operations, reduce costs, and enhance overall healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
The rise in adoption of medical wearable software development opens a whole new market of opportunities in the healthcare industry. Wearables can help patients track their data and remind them to take medications. and for healthcare facilities that means offering more accurate treatment protocols and potentially reducing hospital visits.
However, some smartwatch app development challenges still remain, particularly concerns about data security, measurement efficiency, and the ease of use. To address these challenges, you need to work closely with hospital decision-makers, engage end users, and make sure to introduce secure software development practices.
Yalantis can help you with the latter: we are an app development company with more than 10 years of experience in healthcare devices and wearable app creating can help you build, integrate, and support your wearable application.
FAQ
How convenient are medical devices for daily use?
Medical devices designed for daily use, such as wearable health monitors, offer significant convenience. They are typically lightweight, user-friendly, and designed to blend seamlessly into daily routines. Features like continuous health tracking, real-time data collection, and wireless connectivity make it easy for users to monitor their health without disruption.
Additionally, many Apple Watch and Wear OS devices sync with mobile apps, providing easy access to data and alerts for any irregularities. Their portability and non-invasive nature enhance adherence to medical advice and support proactive health management, making them highly convenient for daily use, and also making medical smart watch software development even more relevant.
How do medical sensors work?
Medical sensors function by detecting specific biological signals and converting them into data that can be analyzed. These sensors often measure parameters such as:
- heart rate
- body temperature
- blood oxygen levels
- and glucose levels.
Medical sensors typically use technologies like photoplethysmography (PPG) for heart rate, thermistors for temperature, and electrochemical sensors for glucose. Once the sensor captures the data, it is transmitted to a connected device, like a smartphone or a central monitoring system, where software processes and analyzes it. This allows for real-time health monitoring, data storage for trend analysis, and alerts for any detected anomalies.
What sensors are used in wearable tech?
Wearable health technology employs various sensors to monitor different health and activity metrics. Common sensors include:
- Accelerometers: Measure movement and orientation to track physical activity and detect falls.
- Gyroscopes: Provide additional movement data, enhancing the accuracy of motion tracking.
- Heart rate monitors: Use photoplethysmography (PPG) to measure heart rate by detecting blood flow changes.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) sensors: Monitor heart activity and detect irregularities.
- Temperature sensors: Measure body temperature for health monitoring.
- Oximeters: Measure blood oxygen saturation levels.
- Glucose sensors: Continuously monitor blood glucose levels for diabetes management.
When creating an app for wearable tech, it’s important to make sure it works seamlessly with the device’s built-in sensors, so users can easily track, view, and understand their health data in real time.
Are wearable devices secure?
Wearable devices can be secure, but their security depends on the measures implemented by mobile app developers, manufacturers, and users. Key security features include:
- Data encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Authentication: Embedding strong authentication methods, such as biometrics or multi-factor authentication, into smartwatch app development process.
- Regular updates: Providing frequent software updates to address vulnerabilities.\
- Secure APIs: Ensuring secure communication between the device and connected applications.
- User awareness: Educating users on best practices, such as setting strong passwords and being cautious with data sharing.
While these measures enhance security, ongoing vigilance is necessary to protect against evolving threats.
What are compliance requirements for building a healthcare wearable device?
Building a wearable health devices involves adhering to several compliance requirements to ensure safety, efficacy, and data protection. Key requirements include:
- FDA approval. In the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) must approve devices for medical use, ensuring they meet safety and effectiveness standards.
- CE marking. In Europe, the device must meet the EU’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) standards and obtain CE marking.
- HIPAA compliance. For devices handling patient data in the U.S., compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is crucial to protect health information.
- ISO standards. Adhering to ISO standards such as ISO 13485 for quality management systems in medical devices.
- Data privacy regulations. Complying with data protection laws like GDPR in Europe to ensure user data privacy and security.
Meeting these requirements in wearable devices development ensures the device is safe, reliable, and compliant with legal standards.
What is wearable app development, and how does it help healthcare?
Wearable app development is the process of building software that connects with smart devices like fitness trackers or medical wearables to collect and monitor health data in real time. At Yalantis, we support wearable device development that helps healthcare providers track vital signs, manage chronic conditions remotely, and improve patient care. Our team also specializes in mobile app development for wearable devices, ensuring smooth data integration with hospital systems and intuitive experiences for both doctors and patients.