Global wearable medical devices market is experiencing steady growth and is predicted to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6% from 2023 to 2030. The main reason for that is that people want to learn more about their health and monitor it, which prompts them to incorporate healthcare wearables in their daily routine.
However, the huge amounts of continuous and real-time patient data generated by health monitoring devices seems to be largely ignored by healthcare providers, even though it could be used for more informed decision-making regarding patient health, or adjusting treatment routines in the comfort of the patient’s home. Why is that so?
The main challenge is integration. Outdated EHR and EMR systems make it slow and expensive to connect hundreds of wearable health devices, and many healthcare providers simply can’t keep up.
In this article, we’ll explore how to integrate wearable health devices with hospital internal systems, compare custom solutions with out-of-the-box ones, and see what opportunities such integration can open for healthcare providers.
Ways to use wearable medical devices in hospital settings

People often use fitness trackers, such as Apple Smartwatch, Google, or Garmin devices, as health wearables, because their latest models can already track various health parameters, including:
- heart rhythm and its abnormalities
- blood pressure parameters
- mobility parameters
- menstrual cycle
- sleeping patterns and irregularities
- breathing parameters
These devices can also remind patients of appointments or medication routines, which help them to be more attentive and engaged in monitoring their health. Collecting data from health wearable devices and using it in the hospital settings can be very beneficial for the following scenarios:
- Continuous patient monitoring. Specialized medical devices like heart rate monitors, glucose sensors, and smartwatches equipped with health-tracking capabilities allow for continuous monitoring of health data while the patient is in the hospital. This data can be transmitted in real-time to healthcare professionals, enabling early detection of issues such as arrhythmias or glucose level spikes, leading to quicker intervention.
- Post-operative care. Patients recovering from surgery can benefit from medical devices that monitor blood pressure, oxygen levels, overall mobility, and other recovery metrics. These devices can alert health care providers to potential complications, such as breathing or heart rate abnormalities, before they become critical, reducing the need for extended hospital stays.
- Remote patient monitoring. Wearable health technologies can be used for patients who are discharged but require remote patient monitoring. By integrating wearable data with the hospital’s EHR system, healthcare providers can monitor patients remotely, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
- Chronic disease management. Wearable medical devices can assist patients with chronic conditions like heart diseases or diabetes by providing them with real-time feedback on their health status. This can improve compliance with treatment plans and encourage healthier lifestyle choices, which is especially important for people with chronic diseases.
- Reproductive health. Digital health monitoring devices like cycle tracking apps, combined with digital health wearable devices like fitness trackers, blood pressure monitors, glucose monitors, and others, can provide continuous tracking of reproductive health parameters and vitals during pregnancy. This will help healthcare providers to proactively address any abnormalities and reduce hospital admissions for pregnant people.
Some hospitals are already using wearable medical devices for patient rehabilitation. For instance, doctors at Cedars-Sinai Hospital in Los Angeles asked their patients to wear Fitbit devices after knee replacements and hip replacements, to encourage them to start walking earlier on after surgery, and speed up their recovery.
Interested in medical device development services?
We design and develop Class II and III medical devices from concept to certification, helping you reduce post-market costs by 30%.
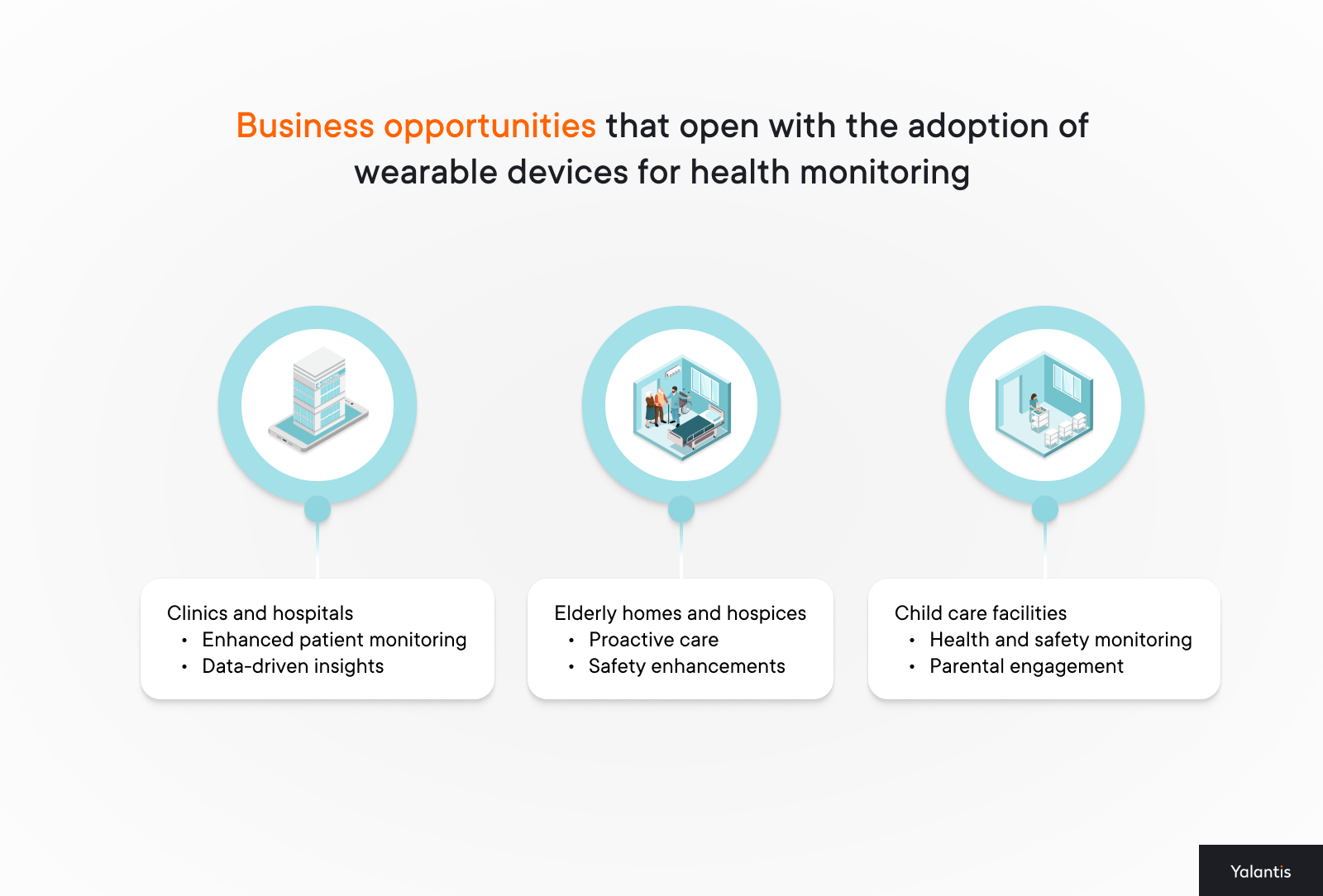
Business opportunities that open with the adoption of wearable devices for health monitoring
While the adoption of wearable medical devices among American patients is growing, 46% of them report that their physicians aren’t including the collected data into their treatment plans.
This is where the healthcare business owners and decision makers can step up and encourage the adoption, often working alongside an IoT software development company, especially given that remote patient monitoring is creating significant business opportunities across various healthcare sectors.
Clinics and hospitals
- Enhanced patient monitoring. Medical wearables allow clinics and hospitals to offer continuous health monitoring services, even after patients leave the facility. This can lead to the development of remote monitoring programs, where patients pay a subscription fee for ongoing care, creating a new revenue stream.
- Data-driven insights. Health monitoring devices provide a wealth of data that can be analyzed to improve patient outcomes. Clinics and hospitals can use this health data to develop personalized treatment plans, increase the efficiency of clinical trials, and participate in research partnerships, further expanding their service offerings.
Elderly homes and hospices
- Proactive care. Wearable health trackers enable the continuous monitoring of elderly and terminally ill patients, allowing caregivers to detect early signs of health deterioration. This proactive approach can reduce hospital readmissions and improve the quality of life for residents, making these facilities more attractive to potential clients.
- Safety enhancements. Wearable medical devices with fall detection, location tracking, and emergency alerts can significantly improve the safety of elderly and hospice residents. Facilities that adopt these wearable technology devices in healthcare can market themselves as providing higher levels of care and safety, potentially attracting more clients.
Child care facilities
- Health and safety monitoring. Wearables in healthcare can be used to monitor the health of children, particularly those with chronic conditions or special needs. This allows childcare facilities to offer specialized digital health services, reassuring parents and increasing their clientele.
- Parental engagement. By providing real-time updates on a child’s health and activity levels, childcare centers can enhance communication with parents. This transparency can be a significant selling point, differentiating the facility from competitors.
Challenges that can hinder the integration of wearable health technology in hospitals

While wearable medical technology offers numerous benefits, its integration into hospital settings is not without challenges. To dive deeper into these challenges and discover solutions, watch our digital transformation in healthcare webinar. These obstacles can be both business-specific and industry-specific, affecting the successful adoption and utilization of wearable technologies in healthcare.
Data security and privacy concerns
Hospitals handle vast amounts of sensitive patient data, and integrating wearable medical devices adds another layer of complexity. Ensuring that the data collected by wearables is securely transmitted and stored to comply with regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. can be challenging. The risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks could deter hospitals from adopting these technologies..
Along with that:
- Choosing a reliable and secure wearable health device can turn into a quest, since there are so many, but not all of them meet the needs of your clinicians and patients
- Wearable tech in healthcare lacks standardized protocols for data encryption and privacy protection across different devices, which can further complicate integration efforts
Interoperability issues
Many hospitals use legacy EHR and EMR systems that may not be compatible with newer wearable medical devices. The integration of wearable data into existing EHR systems can require significant investments in IT infrastructure and custom healthcare software development.
Also, the lack of standardization among wearable technology for healthcare that we mentioned earlier, can exacerbate interoperability challenges due to various data formats and communication protocols. This hinders seamless data exchange between health monitoring devices and hospital systems.
Cost and resource allocation
The initial investment in health wearable technology, including device procurement, IT upgrades, and staff training, can be significant. Smaller hospitals or those with limited budgets may struggle to justify these costs without clear evidence of a return on investment.
Plus, the rapid pace of technological advancement means that wearable health monitoring devices can quickly become outdated, requiring continuous investment in newer tech to stay competitive.
Need a reliable tech partner for IoT medical device development?
Step-by-step guide on integrating health monitoring wearable devices into EHR system
Now, let’s talk about the integration of medical wearable technologies into hospital EHR systems. While the complexity of this process varies from clinic to clinic, it still has a defined set of steps that you need to take to ensure the integration goes smoothly.
This guide, crafted by Yalantis’ experts, will take you through each step in detail
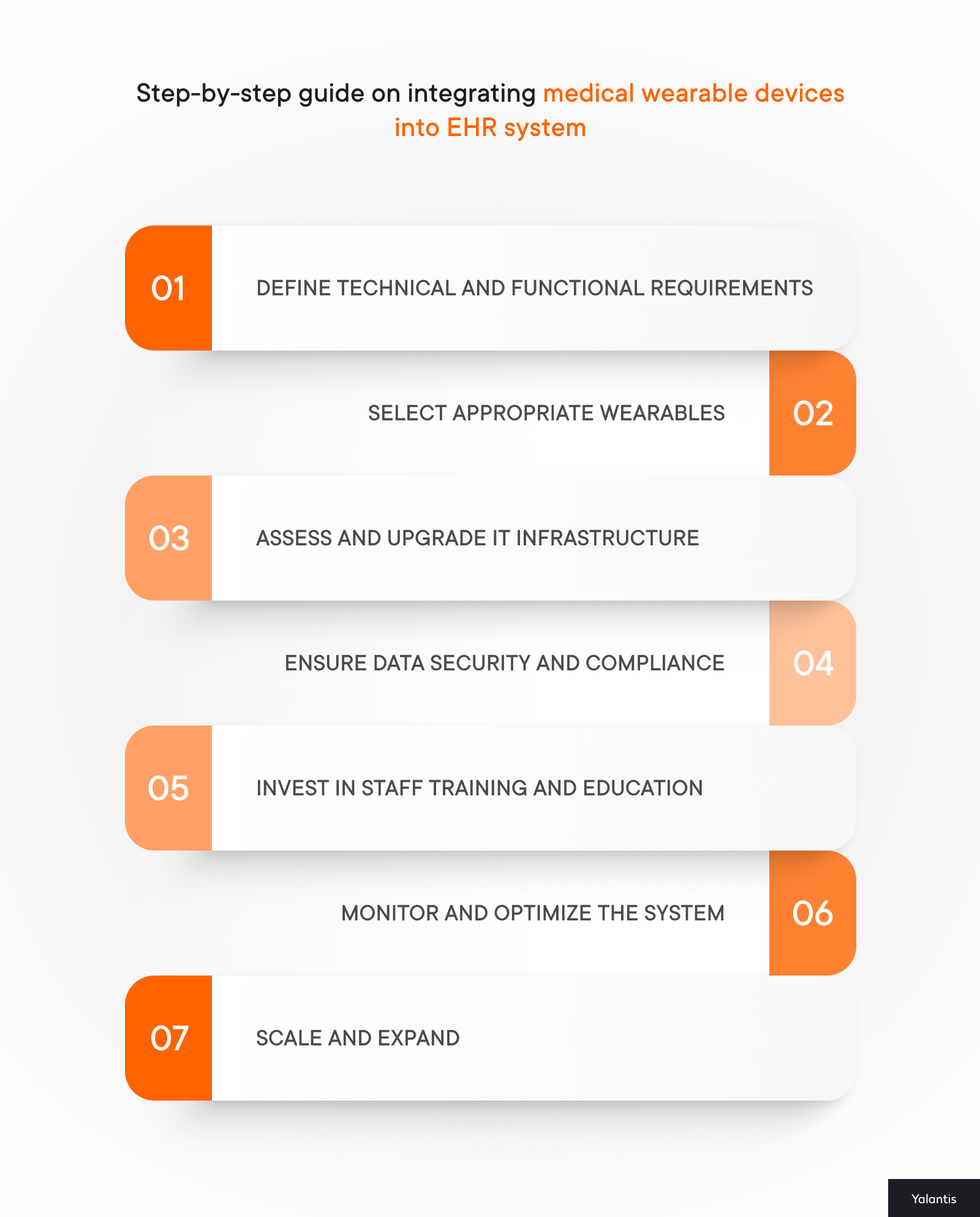
#1 Define technical and functional requirements
Before starting the integration process, you need to state goals and requirements for the integration, as they will impact the further preparations and steps.
The requirements may include:
- the types of data you need to collect (e.g., heart rate, glucose levels)
- the frequency of data collection,
- how this data will be used within the EHR system
To make sure you collect all the requirements, interview different stakeholders, including healthcare providers, IT staff, and patients.
#2 Select appropriate wearables
Not all health wearable devices are suitable for integration with EHR systems, which is why it’s important to evaluate the devices based on compatibility with your existing health system. Also, consider factors like data accuracy, battery life, and ease of use for patients.
Once you’ve selected the medical wearable technology in healthcare, conduct a pilot test with a small group of patients to assess the effectiveness of the selected devices. During this phase, gather feedback from both patients and healthcare providers to identify any issues or areas for improvement.
By the way, partnering with a team that offers wearable app development services can also help you align device functionality with your clinical and technical needs.
#3 Assess and upgrade your solution and IT infrastructure
Evaluate the current solution in use, if you have any, and the overall IT infrastructure, to determine if it can support the integration of wearable technology. This includes:
- evaluating the capacity of your servers
- assessing network bandwidth
- checking the ability of your EHR system to handle the additional data load.
If necessary, upgrade your IT infrastructure to ensure it can support the integration. This may involve expanding server capacity, enhancing network security, or upgrading to a more advanced EHR system that is compatible with wearable healthcare devices. Ensuring scalability is also crucial to accommodate future expansions or the addition of new wearable technology health devices.
#4 Ensure data security and compliance
Patient data security is essential when integrating hospital wearable technology into EHR systems. Here are some tips to achieve it:
- Set up strict access controls, such as multi-factor authentication or role-based access controls, to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the data collected by wearable health technology.
- Ensure that all data transmitted from a wearable device to the EHR system is encrypted to protect patient privacy and comply with regulations such as HIPAA.
- Check and review standards for data interoperability such as those set by the Health Level Seven (HL7) organization, to avoid connectivity issues and data breaches.
Plus, wearable technology development is subject to numerous compliance regulations, from the international regulations to regional and local laws. Here are the main regulations and approvals you need to meet to be able to sell your medical devices across different regions and globally:
- United States: Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval, HIPAA compliance
- Canada: Medical Devices Compliance Program (MDCP), PIPEDA compliance
- Europe: EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device Regulation (IVDR), GDPR.
- Australia: Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), Privacy Act 1988
- International: ISO 14971, ISO 10993, IEC 62304, GDPR
As you can see, there’s a lot of regulations to take into account, that’s why your best best would be consulting with a compliance specialist that is competent in the compliance requirements of a region you want to operate in.
Compliance mistakes cost more than you think
Cut rework and service costs before they happen with our free ISO 13485 + FDA compliance guide.
#5 Integrate wearable devices with the EHR System
If you have an EHR vendor, you can contact them and create the necessary interfaces for data exchange between the wearable devices and the EHR system. If you work with the external development team, they typically handle these processes for you.
Integration interfaces typically include:
- application programming interfaces (APIs)
- middleware that translates the data from a wearable device into a format that the EHR system can understand
- file transfer protocols (FTP)
Before full deployment, thoroughly test the integration to ensure that data is being accurately and consistently transmitted from the wearable technology to the EHR system.
#6 Invest in staff training and education
A big part of successful integration and adoption of a new wearable healthcare technology lies in the comprehensive training of its end users.
Provide instructions and workshops to health care providers on how to use the new system, including:
- how to interpret the data from a wearable device
- how to set up alerts
- how to integrate this information into their decision-making process.
Training should be tailored to different user roles, ensuring that each team member understands their specific responsibilities.
Along with clinic staff training, make sure to educate patients on how to use the wearable healthcare technology effectively:
- provide instructions on wearing the device correctly
- teach them how to sync data with the EHR system
- make sure they’re aware of the ways their data will be used by health care providers.
Offer support resources such as tutorials, help desks, or online guides to assist patients in this process.
#7 Monitor and optimize the system
After the integration is live, make sure to monitor the system to ensure it is functioning as intended. This includes tracking data accuracy, system performance, and user satisfaction. Establish a system for reporting and addressing any issues that arise.
You might also want to collect feedback from health care providers and patients to identify areas for improvement. Regular feedback loops can help you refine the system, address any pain points, and enhance the overall user experience.
As technology evolves, so too should your integration. Regularly update the wearable devices, EHR system, and associated interfaces to ensure they remain compatible and secure. This might also involve integrating new types of wearable devices or expanding the system’s capabilities to include additional data types or advanced analytics.
#8 Scale and expand
Once the integration is successful in one department or patient group, consider scaling wearable healthcare technology to other areas of the hospital. This could involve integrating additional types of wearable technology in healthcare or expanding the use of the system to include more complex data analysis.
Learn how we built and connected compliant medical devices with clinic systems across the U.S.
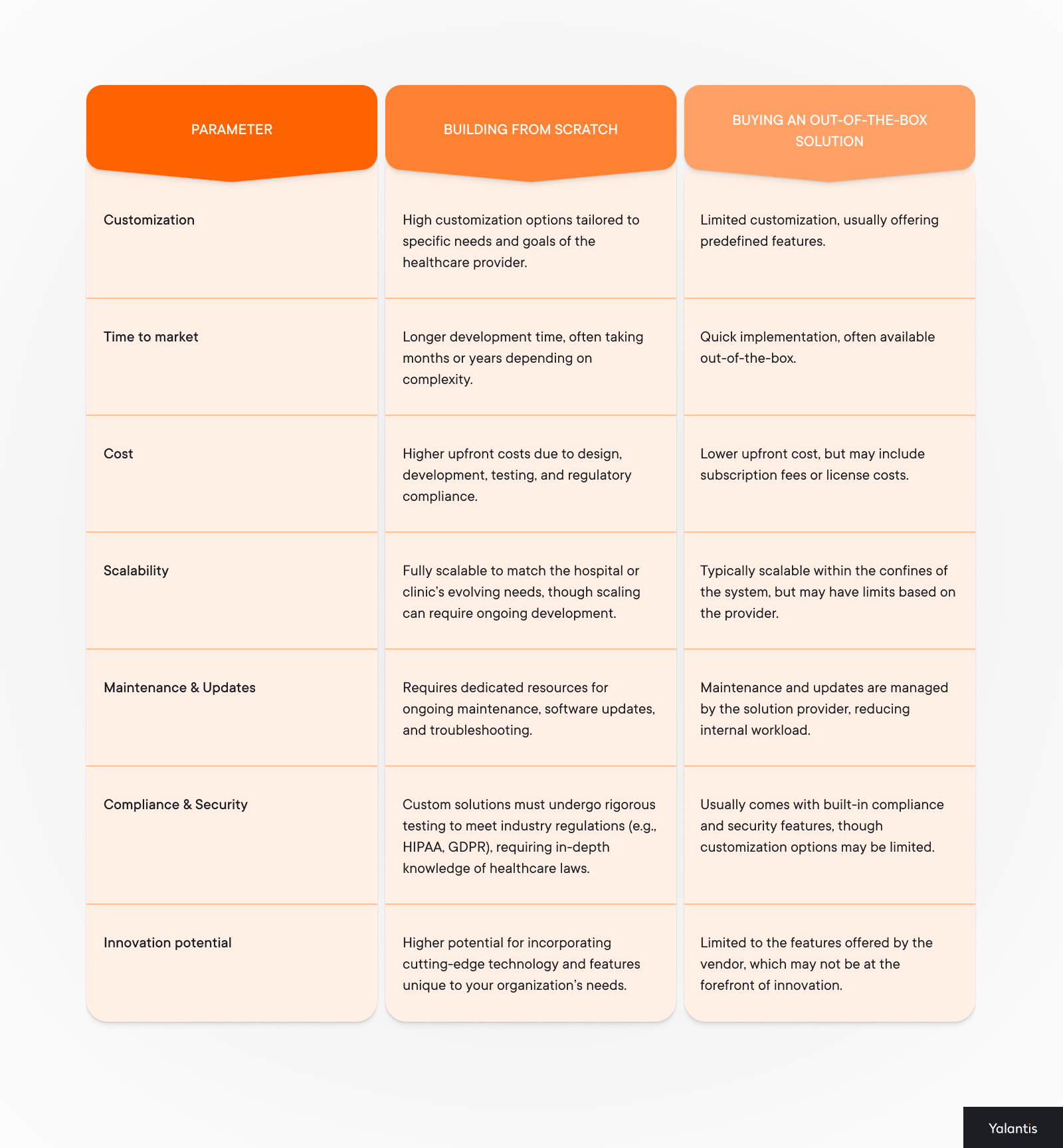
What’s better: building wearable devices in healthcare from scratch or buying a ready-to-use solution?
Now, after seeing all those steps and calculating the time and resources for the integration, you might have thoughts about buying a ready-to-use solution that you can launch right away and augment your EHR system with new capabilities.
While there’s no “one size fits all” when it comes to transforming a healthcare facility, making an informed decision is always a good start. That’s why we compared both approaches to medical wearables integration in the table below, so you can make your choice.
Why partner with Yalantis for building medical wearables and integrating them into your hospital’s EHR system?
Yalantis is a software development company with more than a decade of experience in developing wearable healthcare technology. We can offer a vast range of services, from developing a firmware for your medical device (firmware development services) to updating your legacy systems and optimizing data flows.
Yalantis’ software developers can apply their expertise in IoT development, prototyping, and integration to help you transform your hospital systems and offer better care to your patients. We will implement industry-specific security practices, ensure compliance with international and local laws and regulations, and help you optimize your costs by repurposing our knowledge and developing only what you need, without any hidden upsells with our IoT solutions for healthcare.
FAQ
What is wearable technology in healthcare?
Wearable healthcare technology, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical-grade monitors, collect real-time data on vital signs, physical activity, and other health metrics.
If you’re wondering what wearables are in healthcare, they’re essentially devices patients wear to help monitor their health continuously. This data helps healthcare providers to monitor patients continuously, detect early signs of health issues, and intervene promptly. Wearables are also empowering patients with insights into their own health, encouraging proactive management of chronic conditions, better lifestyle choices and health outcomes as a result.
Are there any downsides to wearable healthcare technology in its current state?
Here are some of the key challenges related to wearables:
- Data accuracy: many consumer-grade wearables are not as precise as medical-grade devices, which can lead to incorrect readings and potential misdiagnoses.
- Interoperability issues: many wearable devices struggle to seamlessly integrate with existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, leading to data silos and inefficiencies.
- Privacy and security concerns: since wearable devices collect sensitive health data, it must be adequately protected against breaches.
- Integration costs: the development of wearable devices and the infrastructure required to support them can be prohibitive for some healthcare providers.
What makes wearable technology and healthcare integration challenging?
The biggest challenge between wearables and healthcare integration is connecting all the data to existing hospital systems, especially older EHRs. But with the right tech and team, it’s absolutely doable.
What do I need to successfully integrate wearable devices at my clinic?
Using wearable devices in healthcare starts with careful planning. To integrate wearable devices at your clinic, focus on these key areas:
- Define objectives. Clarify what you aim to achieve, such as improved patient monitoring or enhanced remote care.
- Select compatible devices. Choose wearables that integrate smoothly with your EHR system and meet your clinical needs.
- Strengthen IT infrastructure. Ensure your IT systems can handle the additional data load, including necessary upgrades for security and capacity.
- Ensure data security. Implement data encryption and compliance measures to protect patient information.
- Train staff and educate patients. Provide training for healthcare providers and educate patients on how to use the devices effectively.
When done right, wearable device data integration in healthcare helps improve care coordination and gives clinicians timely access to real-time patient data, making it easier to make informed decisions.
What are the benefits of wearable technology in healthcare?
The use of wearable technology in healthcare today helps doctors track patient vitals in real time, catch health issues early, and make more informed treatment decisions — all without needing constant hospital visits.
Can you help with medical wearable software development?
Yes, we build custom software for wearable medical devices and ensure it connects smoothly with hospital systems like EHRs.