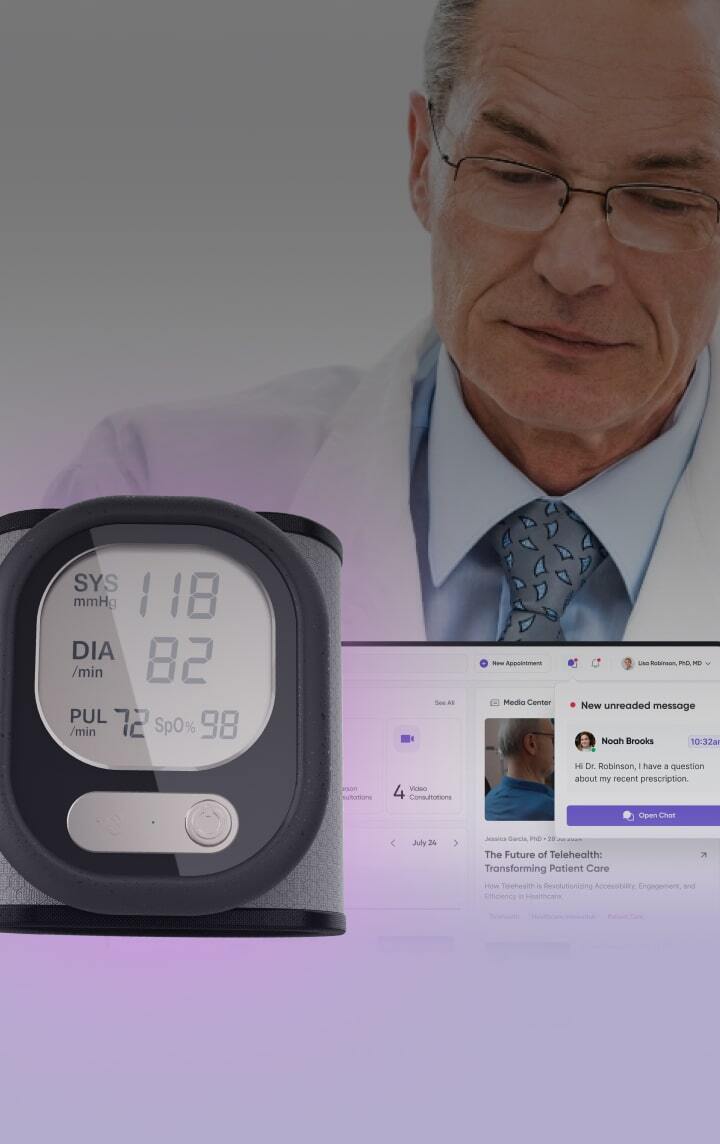
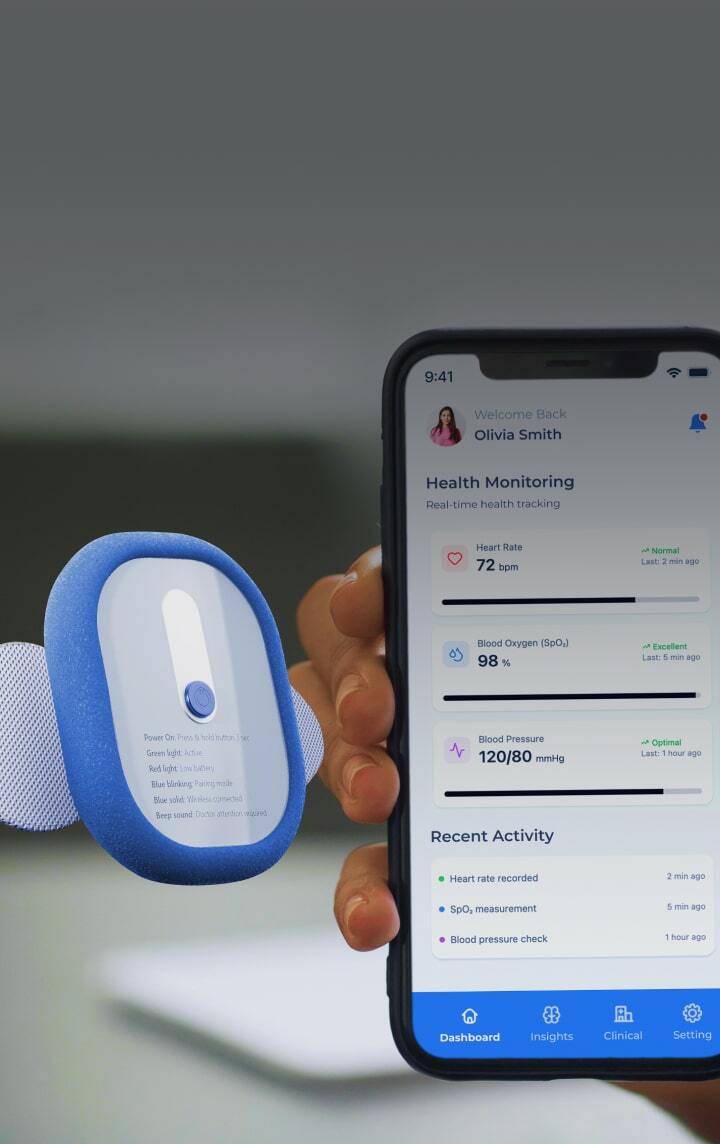
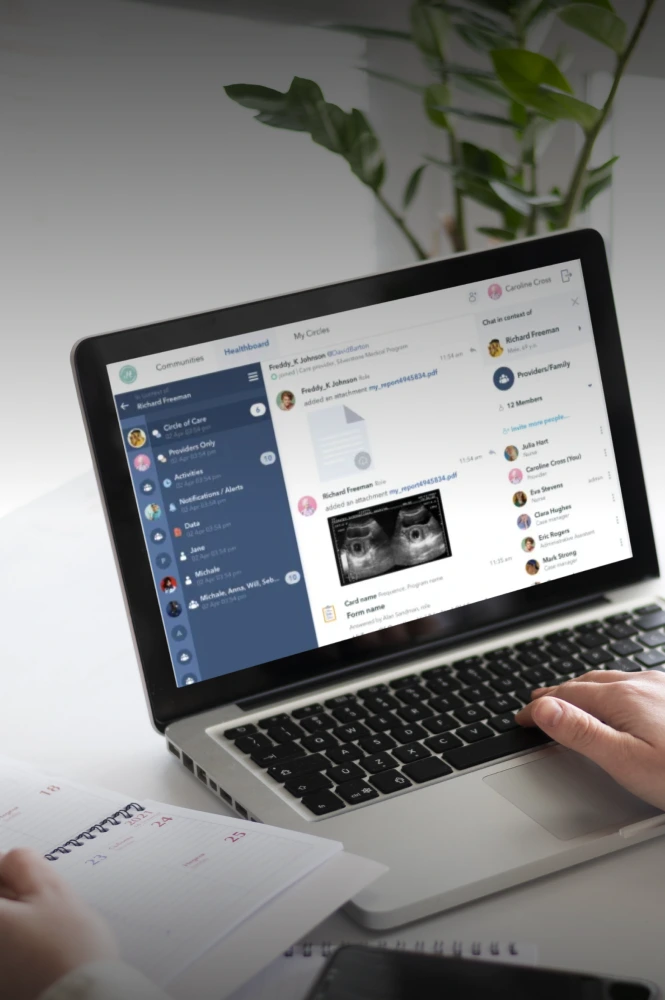
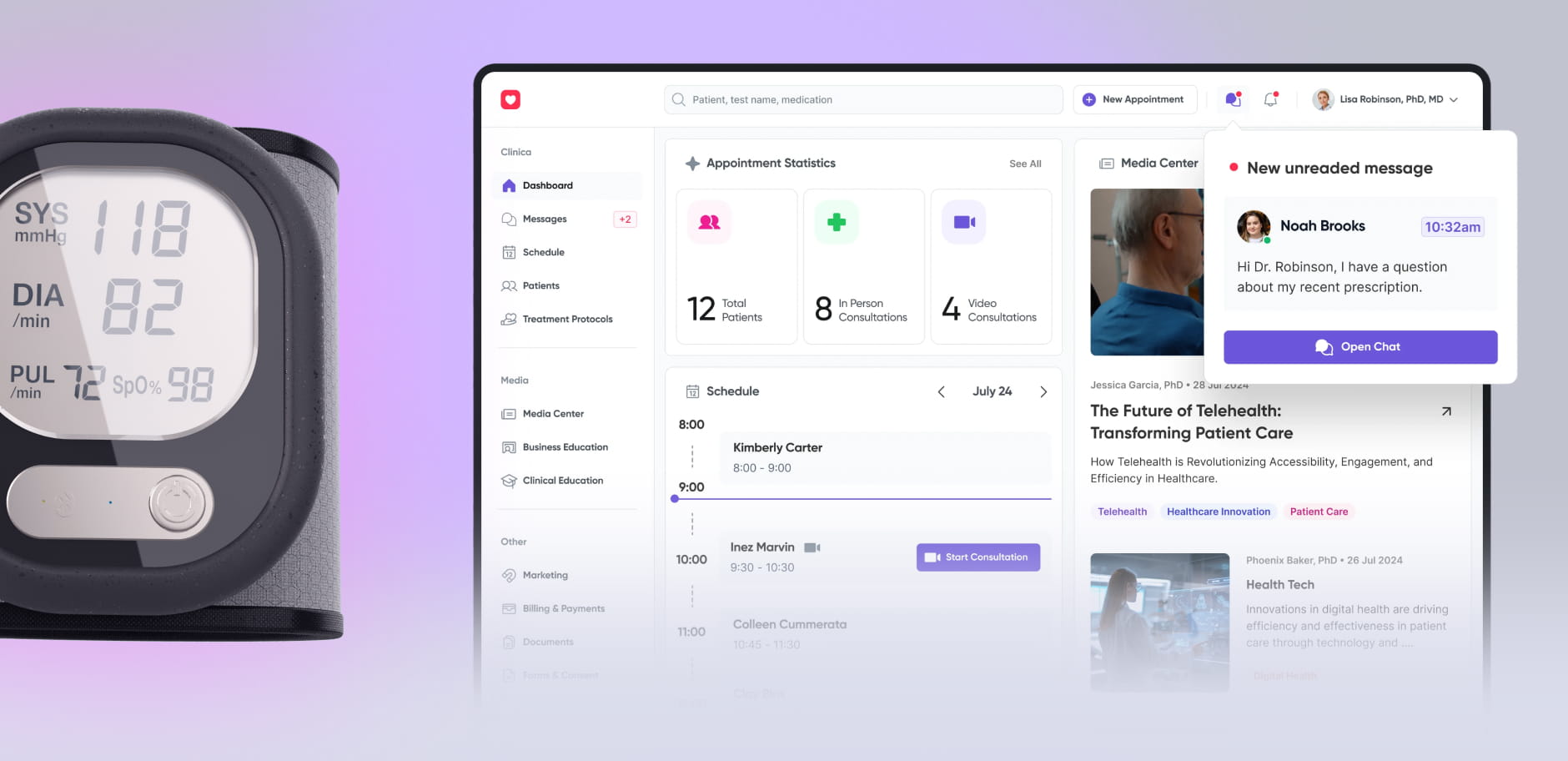
Medical devices design &
development services
We design and develop Class II and III medical devices from concept to certification, helping you cut time-to-market by 6 months and reduce post-market costs by 30%.
Years in healthcare
Built-in compliance
FDA & CE approvals
Experts
ISO Certified QMS
End-to-end medical device design and development
Types of Class II and III devices we work with
Technologies we work with
-
Rust
-
C
-
C++
-
Kotlin
-
Bootloader
-
Linux Kernel
-
AWS IoT
-
Arduino
-
ESP32
-
STM32
-
NRF52
-
Zephyr
-
LoRaWAN
-
MQTT
How we work on your certified medical device
-
Discovery & planning
In the first phase, we provide you with a clear roadmap that reflects your goals and meets regulatory requirements.
-
Architecture & prototyping
Building on that plan, our engineers deliver early prototypes and system design so you can see how the product will work before full development.
-
Development in iterations
Once the foundation is set, you’ll see steady progress in short cycles, with working features delivered and refined at each step.
-
Testing & compliance
Alongside development, every stage includes thorough testing and documentation, giving you dependable results and alignment with FDA, MDR, and ISO standards.
-
Launch & certification
With a fully tested product in hand, our experience with global submissions ensures it’s prepared, documented, and supported through approval.
-
Post-market support
After release, you can count on ongoing updates, monitoring, and maintenance to keep your device safe and compliant.
What our clients say
Why partner with Yalantis
Proven track record
We deliver software for Class II & III medical devices, leveraging 15+ years of experience to handle safety-critical complexity where failure is not an option.
Pioneering Rust expertise for medical devices
Eliminate memory vulnerabilities in device firmware using Rust. We ensure 99.99% uptime and solving safety challenges that generalist dev shops cannot handle.
Rapid medical device engineering staffing
Scale your R&D in 2-4 weeks with specialized medical device engineers. We ensure critical domain knowledge remains consistent throughout the device lifecycle.
Audit-ready medical device security & compliance
An ISO 13485-ready partner aligning device architecture with IEC 62304 and FDA standards from day one to streamline your certification.
End-to-end medical device synergy
We bridge hardware and cloud, unifying low-level firmware, sensor data, and mobile apps into a seamless connected medical device system.
Engineered for medical device profitability
Maximize margins by optimizing device BOM costs and workflows. We ensure your product makes business sense from prototype to mass production.
Medical devices design & development insights

How to Build a High-Quality IoT Medical Device (MIoT)
Learn what’s under the hood of the innovative IoT medical devices and how high-quality prototyping, design, quality assurance, and compliance with rigorous regulations define the future of your product.

Top Medical Device Companies Leading Global Healthcare Innovation

Rust for Medical Devices: Certified Software for Safety-Critical Systems
Explore how Rust can enhance medical device software with memory safety, performance, and reliability, helping developers build secure and dependable embedded systems.
FAQ
How do you handle integration issues with existing healthcare systems?
Challenges in medical device software development often originate from poor vendor documentation or integrating multiple devices. We handle this by working with vendors directly or suggesting better-documented alternatives. For multi-device setups, we merge and normalize data to ensure smooth processing. Every project is unique, so issues may vary.
Can you assist with FDA or MDR compliance for medical device software?
Yes. We provide software design for medical devices in line with FDA and MDR regulations, as well as ISO 13485 and IEC 62304 standards, to support smooth approvals and safe releases. That applies to software development for medical devices as well.
Do you develop Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)?
That’s what we do! We offer medical device software engineering for SaMD products, from risk analysis and UI design to cloud connectivity and compliance.
Can you integrate medical devices with EHR or hospital systems?
We can. Yalantis is a medical device design firm that also delivers medical device interoperability services, supporting integration with EHRs, hospital platforms, and HL7/FHIR standards.
How do you ensure the interoperability of connected medical devices?
We develop medical device software solutions that standardize and synchronize data across various devices, so the data exchange is smooth and compliant.
Do you provide validation and verification services for medical software?
Yes, we do it as part of our medical device software development services. We conduct strict verification and validation (V&V) testing to ensure software safety, reliability, and compliance.
What is your experience with healthcare and medtech interoperability?
We’ve delivered medical device engineering services for all classes of FDA-approved devices and built custom medical device solutions from scratch solutions from scratch. The experts from Yalantis develop medical device software for diagnostics, remote monitoring, and chronic disease management, offering medical device software consulting and ongoing medical device software outsourcing when needed. This makes us a long-term partner for healthcare companies that require seamless data integration and dependable outcomes.
Contact us

got it!
Keep an eye on your inbox. We’ll be in touch shortly
Meanwhile, you can explore our hottest case studies and read
client feedback on Clutch.

Nick Orlov
IoT adviser
How to get started with IoT development
-
Get on a call with our Internet of Things product design experts.
-
Tell us about your current challenges and ideas.
-
We’ll prepare a detailed estimate and a business offer.
-
If everything works for you, we start achieving your goals!