
How to build healthcare software that can obtain ONC Health IT Certification
Software development companies are eager to build healthcare IT products that improve patient engagement, clinical workflows, and data sharing between care providers and consumers. But the variety of available solutions puzzles medical organizations who are seeking the most appropriate one to enhance productivity and daily operations.
Steep price tags associated with implementing health IT projects, with some exceeding $100 million, make this decision even more grueling for organizations. They need to make sure the product they choose is 100 percent failsafe, user-friendly, and secure, meeting their clinical needs and all federal requirements.
How can you as a software provider promise all of the above? The answer is through obtaining ONC Health IT Certification. There are also other perks you’ll get as a result of having your product certified:
Quality mark. While deciding on healthcare software, healthcare organizations take into account many factors including colleagues’ feedback and the organization’s specific needs. But knowing that a product is certified may be critical in making the final decision, as certification indicates quality.
Wider adoption. Certification is mandatory for healthcare providers working with Medicare and Medicaid and participating in Quality Payment Programs. To regularly receive incentives, it’s obligatory for clinics to purchase and adopt certified electronic health records (EHRs).
Extensive publicity. Your brand and certified products will appear not only in the list of ONC-certified software but also in the most reputable medical blogs and press releases.
Yalantis has experience helping our clients obtain ONC certification. In this article, we’ll talk about how to get certified in healthcare based on our experience. But let’s first go over some history to understand the purpose and logic of ONC certification.
NEED ASSISTANCE IN OBTAINING ONC CERTIFICATION?
We have vast experience in helping our healthcare clients comply with industry regulations
It all started with the quick achievement of EHR adoption
In the early 2000s, the US government recognized the huge potential of electronic health record (EHR) systems for improving medical workflows and ensuring that patient data is available for clinicians. The promise that EHR systems would lead to better treatment convinced US lawmakers that they needed to achieve widespread adoption of EHR systems at the national level.
In 2004, the US government created the Office of the National Coordinator (ONC) of Health Information Technology, an entity responsible for managing work on a national certification program for EHR software.
In 2009, Congress passed the HITECH Act. According to its tough terms, if Medicare eligible professionals didn’t adopt EHR technology, their Medicare physician fee schedule for covered professional services would go down by one percentage point each year beginning in 2015.
As a result of this act, 94 percent of US hospitals were using an EHR system in 2017. The diagram below shows the effectiveness of the HITECH Act in promoting EHR adoption. It’s the reason why this technology became well-established in the United States.
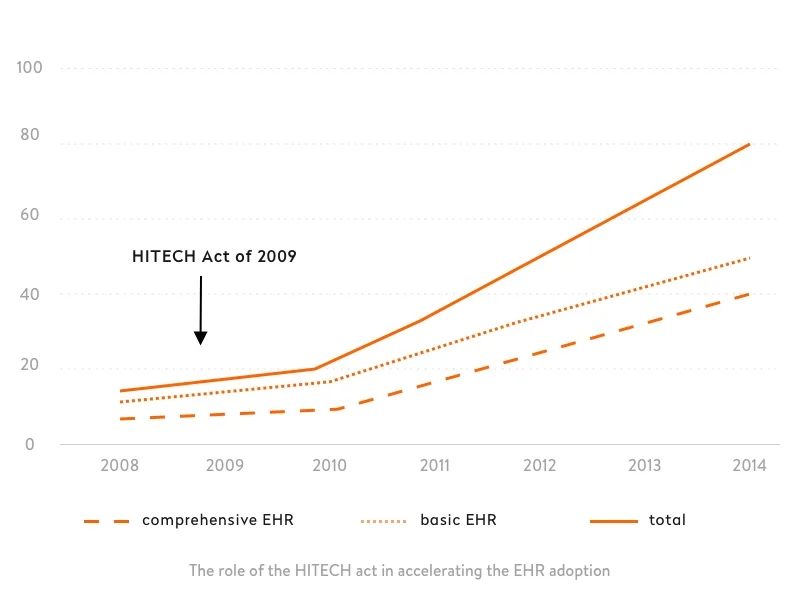
Not just adoption but meaningful use
The aim of the HITECH Act was not just adoption but “meaningful use” of EHRs, which requires ensuring crucial improvements in care. To support the meaningful use of EHRs, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) allocated federal funds and established payment programs to reward clinicians for meaningful use through the Medicare and Medicaid Promoting Interoperability Programs.
In 2010, the ONC established a Health IT Certification Program. EHRs and health IT modules (EHR-integrated solutions or units that together constitute a health IT system) that have passed this certification are included in the Certified Health IT Product List (CHPL).
To take part in the Medicaid and Medicare Promoting Interoperability Programs, clinicians have to adopt one of the software solutions in the CHPL, which contains all certified health information technology products. To become certified and get on the list, software has to be successfully tested by the ONC Health IT Certification Program.
Through the Health IT Certification Program, the US government creates a favorable environment for improving the quality of care, which benefits patients and the whole health system. The program also allows healthcare providers to facilitate their processes, increase their reputations, and participate in payment programs (or at least avoid penalties for not participating).
Having recognized the benefits of the Health IT Certification Program, we’ll discuss its structure, criteria for obtaining certification, and the certification process.
ONC Health IT Certification Program in a nutshell
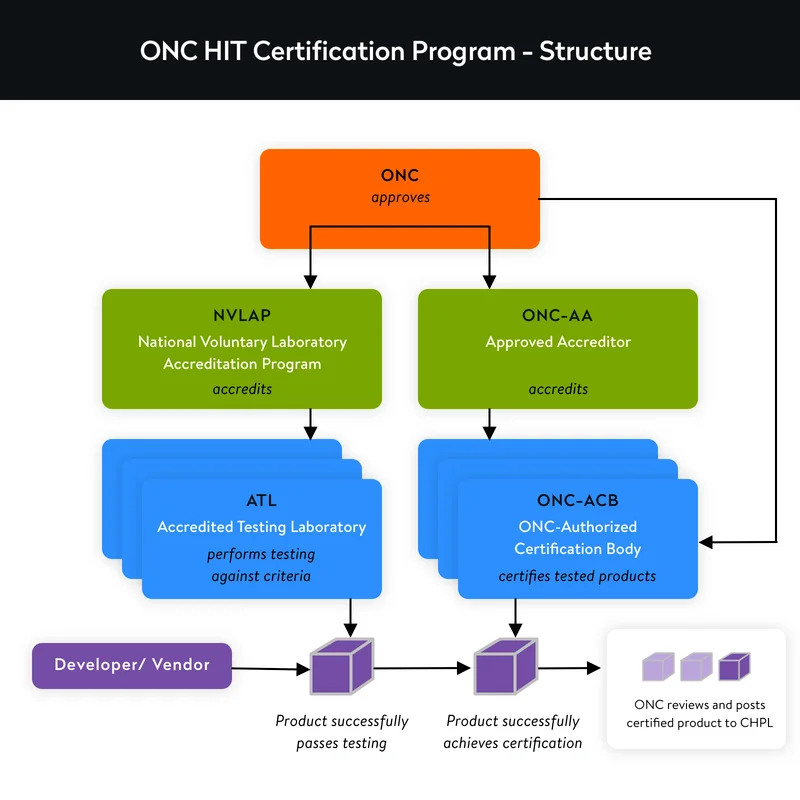
The Health IT Certification Program is based on a third-party conformity assessment scheme and has the following structure.
Certification program participants
The ONC doesn’t directly conduct conformance testing or offer certification. Rather, this organization cooperates with third parties that it assesses, approves, and authorizes to do this work on its behalf.
These are the participants in the certification process:
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). As the HITECH Act requires, NIST and the ONC together create requirements, cases, and tools related to software testing.
National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program (NVLAP). Administered by NIST, NVLAP is in charge of accrediting and supervising testing laboratories participating in ONC Health IT Certification Program.
ONC-Authorized Testing Laboratory (ONC-ATL). An NVLAP-accredited ONC-ATL conducts health IT testing to identify compliance with ONC standards and certification criteria based on the ONC-approved test method.
ONC-Authorized Certification Body (ONC-ACB). This entity certifies health IT products according to test results delivered by ONC-ATLs. The ONC-ACB also adds results to the CHPL and is in charge of monitoring certified software. Some ONC-ACBs like Drummond Group, ICSA Labs, and SLI Compliance are also ONC-ATLs, meaning they can test your software, define its compliance, certify it, and publish it on the CHPL.
ONC-Approved Accreditor (ONC-AA). The ONC approves an entity for a three-year term to accredit and oversee ONC-ACBs according to the program requirements.
Health IT developer. These participants develop software and offer it to be tested and certified in accordance with the program.
What you need to know to ensure compliance with HIPAA
READ THE POSTCertification criteria your software has to meet
Let’s talk about how to get ONC certification. The ONC has issued three editions of certification criteria. The latest 2015 Edition Health IT Certification Criteria integrates previous rules and is based on improved criteria, standards, and implementation requirements. All eligible hospitals under the Medicare and Medicaid Promoting Interoperability Programs must follow the 2015 Edition.
Certification criteria are divided into eight categories.

1. Clinical processes
This category includes functionality you need to implement within your software to meet the following requirements:
- Computerized provider order entry (CPOE) for medications, laboratory, and diagnostic imaging
- CPOE drug checks regarding medication interactions to facilitate medication safety and effectiveness
- Capturing accurate patient demographic data
- Creating accurate lists of patients’ problems, medication allergies, and current and previous medications for improved monitoring and visibility
- Clinical decision support tools
- Drug-formulary and preferred drug lists to minimize unexpected medication costs
- Recording patients’ use of tobacco to tailor care plans
- Capturing patients’ family health histories to enhance clinical decision-making
- Offering patient-specific education sources like videos, posts, and other patient-tailored content for improved patient engagement
- Integrating device identifiers (UDIs) to track the performance of patients’ implantable devices
- Capturing social, psychological, and behavioral data to form a more complete picture of a patient’s health
2. Care coordination
As a rule, each member of a healthcare team has particular, limited interactions with a patient depending on their expertise. As a result, the team’s perspective on the patient’s state might become fragmented into disconnected facts and symptoms. To obtain ONC certification, software has to provide a holistic view of a patient’s health.
This might be achieved by integrating and organizing protected health information and improving its sharing between all authorized providers engaged in a patient’s treatment. For instance, EHR alerts can notify providers of updates related to a particular patient, enabling them to see the whole picture of the patient’s health and what medical procedures the patient has undergone.
3. Electronic clinical quality measures
EHRs have to provide electronic clinical quality measures (eCQMs). These are tools that help to estimate and monitor the quality of a healthcare provider’s services. eCQMs should cover the following aspects of patient care:
- Patient and family engagement
- Patient safety
- Care coordination
- Population / public health
- Efficient use of healthcare resources
- Clinical processes / effectiveness
Healthcare software applying for ONC certification has to record, export, and import CQM data, accurately calculate eCQM results, report to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services if the software is intended to be used for CMS reporting, and enable doctors to filter CQM results.
4. Privacy and security
Privacy and security certification criteria require developers to guarantee that their software protects electronic protected health information (ePHI) whether it’s stored or transmitted and that only authorized individuals can access ePHI.
The ONC, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR), and other HHS agencies have developed a number of resources to help you ensure your EHR software meets privacy and security requirements. They include tools, guides, and documents to help you ensure HIPAA compliance and meet other federal regulatory requirements.
5. Patient engagement
According to patient engagement criteria, patients have to be able to proactively participate in their own treatment. This facilitates better health outcomes and results in better care. To get ONC-certified, developers have to enable patients to securely communicate with doctors and view, download, and transmit their health data.
The ONC Patient Engagement Playbook provides tips and best practices for patient engagement that the ONC has received from healthcare providers.
6. Public health
The public health criteria in the 2015 Edition require healthcare providers to take preventive measures and diagnose and treat a whole population rather than one individual at a time. Public health criteria require transmitting public health data to immunization registries, syndromic surveillance systems, cancer registries, etc.
7. Health IT design and performance
Design and performance criteria for a software system include:
- Automated numerator recording and automated measurement calculations
- Safety improved design
- Quality management system
- Accessible design
- Transitional care when moving a patient from one setting of care to another
- Data exchange via API technology
8. Electronic exchange
This category refers to healthcare interoperability. It covers data access, data sharing, and cooperative use of data in a coordinated manner. You can meet electronic exchange criteria by using data exchange architectures, application interfaces (APIs), and specific standards like HL7.
For details on what functionality an EHR has to have to meet clinical process, privacy and security, patient engagement, and interoperability criteria for certified EHR software, read how to develop an EHR system. Yalantis also has experience integrating with EHR systems, such as Epic, Cerner, and other systems, and setting up secure data exchange.
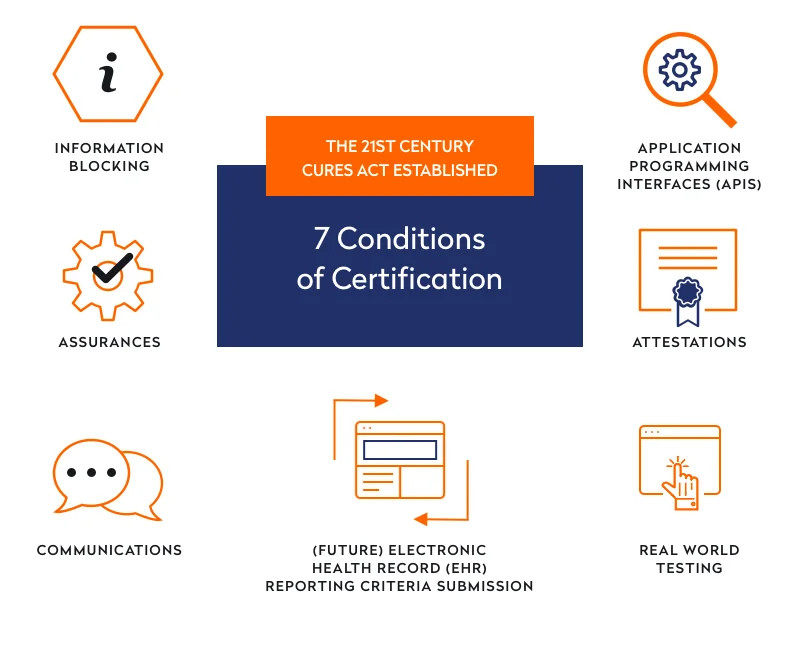
To help eHealth developers pass the ONC Health IT Certification, the ONC and HHS developed seven conditions for Electronic Health Record certification and maintenance certification requirements.
Conditions of software certification established by the 21st Century Cures Act Final Rule
The final rule by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) implementing parts of the 21st Century Cures Act provides the following seven conditions of certification:
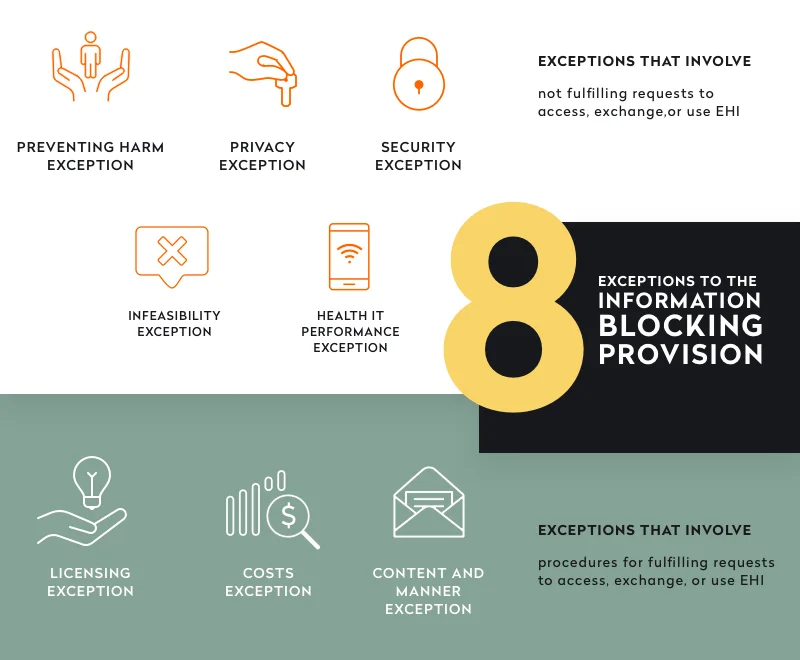
1. Information blocking
The information blocking condition bans from obtaining certification all health IT developers who intentionally withhold patient health information either between providers or between a provider and a patient. But what is the definition of “intentionally”? In the final rule, the ONC highlights eight exceptions that are not considered information blocking. Check them out in the image below.
2. Assurances
This condition requires a developer to prove that their software doesn’t block the appropriate exchange, access, and use of electronic health information (EHI). To fulfill this condition, developers have to provide technology certified according to the EHI export certification criterion if their product stores EHI.
3. Communications
Developers can’t prohibit or restrict communications related to such aspects of software performance as:
- Usability
- Interoperability
- Information security
- User experience
- Developers’ business practices regarding the exchange of EHI
- The way a user has used the healthcare software
4. Application programming interfaces (APIs)
The final rule also expects healthcare providers and device developers to support the use of third-party apps and APIs. The ONC also requires that API follow FHIR Release 4. This is the latest version of the FHIR Standard. Check the recent API Resource Guide by ONC for details on requirements regarding API implementation.
5. Real-world testing
Developers must successfully test their software in the real world to check for interoperability in the types of settings where their software will be used. Developers have to annually submit real-world testing plans to the ONC-ACB so these plans will be available on the CHPL. The next step is to annually submit real-world testing results that are also added to the CHPL.
6. Attestations
This condition obliges developers to attest that they meet all the Conditions and Maintenance of Certification requirements. Developers have to submit their attestations every six months, and there is a 30-day window for submissions. The first window will be opened on April 1, 2022.
7. (Future) EHR reporting criteria submissions
Developers must submit reporting criteria for their certified software under the EHR Reporting Program, which is currently under development. The ONC plans to implement the related Condition and Maintenance of Certification requirements for EHR certification in future rulemaking.
Developers should keep in mind that the deadline for complying with Information blocking requirements is April 5, 2021. The deadline for meeting requirements around standardized API features is December 31, 2022.
Now that you know the criteria and conditions of Health IT Certification, let’s touch upon the certification process itself.
Brief overview of the certification process
The 2015 Edition Health IT Certification test method includes test procedures, test data, and associated test tools for developing new health IT modules. The certification process performed by an ONC-Authorized Testing Laboratory includes an assessment of testing artifacts to check if all requirements are met once all necessary contracts and testing materials are obtained.
Once the estimation process is over and if there are no problems with the submitted documentation, the software is certified and all related information is posted on the CHPL.
ONC-ACBs then perform further surveillance to check if the software they have certified keeps functioning as required. While software remains certified, healthcare providers can use it.
A few tips to go based on Yalantis’ experience:
- If you need to obtain certification for an already developed product, first analyze its compliance with ONC requirements. This will help you identify which requirements have already been met, which parts of the product need improvement, and which components you need to add to the system.
- Follow the Guideline for Using Cryptographic Standards and the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines instead of using self-made data encryption systems. This will ensure you fully comply with federal requirements.
- Keep in mind that there are no documented descriptions of how you should build or implement modules and functionality. To fully meet certification requirements, choose those technical and usability principles you consider the most appropriate for your specific software product.
As you can see from the explained above, building healthcare software systems capable of obtaining Health IT Certification is challenging and requires a complex approach. A minimal requirement for certification doesn’t exist and there’s a set of requirements you’ll have to meet. Need a software development partner who can provide related consulting, is experienced in creating mature healthcare products, and is informed in all the technical and compliance peculiarities of Health IT Certification? Yalantis would be a wise choice.
Seeking an experienced healthcare software partner?
You’re in the right place
Rate this article
5/5.0
based on 1,154 reviews



