Many companies pursue warehouse automation with a singular focus on mechanizing physical tasks. The logic appears sound: replace manual labor with robotics to increase the speed of moving goods.
This strategy, however, frequently overlooks the foundational problem that plagues logistics. Automating the movement of poorly tracked items only creates faster, more expensive chaos.
A more effective approach grounds automation in a foundation of high-fidelity data. The combination of intelligent sensing technologies and machine learning creates a precise, real-time digital picture of the physical warehouse.
Take smart sensors, RFID tags, BLE beacons, and cameras, add AI/ML analytics, and you can benefit from real-time inventory monitoring and smart warehouse automation. Powered by these technologies, warehouse robotics, digital twins, and inventory management systems can ultimately improve inventory visibility, speed up order fulfillment, and reduce costs.
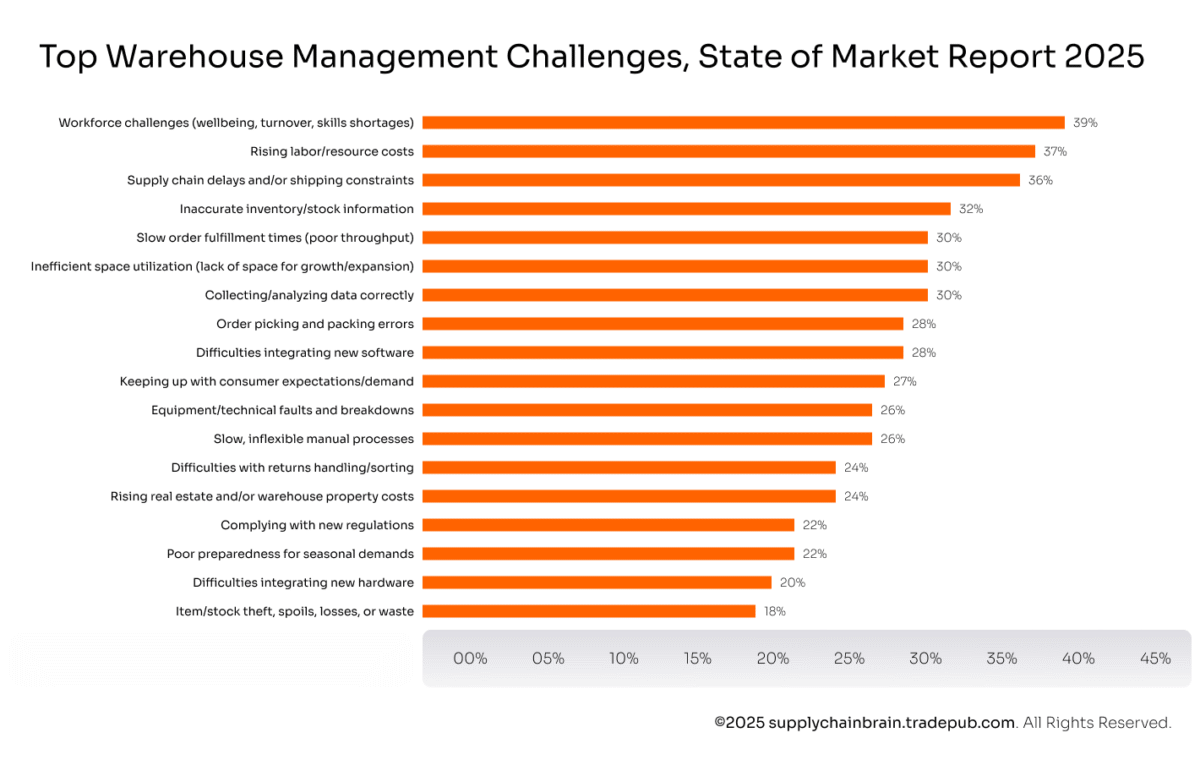
Automation is already everywhere in logistics and warehousing, with half of industry players already having at least 50% of their operations automated. Yet, a third of warehouse operators (32%) still don’t have accurate data on their inventory. Around the same share (30%) face slow order fulfillment times or inefficient space utilization.
IoT and AI/ML hold the key to overcoming these and other challenges. In this article, we’ll leverage our experience in full-stack IoT services to break down:
- How AI and IoT are used in inventory management and warehouse operations
- Which IoT components are integral to smart warehouse automation
- How IoT and AI/ML can benefit your business
“The IoT technology itself is versatile, but it requires AI/ML analytics to deliver the cost savings and efficiency gains you expect. For instance, AI/ML can power predictive analytics for accurate demand planning. It also enables digital twins for stress-testing warehouse operations and making informed decisions to improve them.”
How Can Technology Enhance Warehouse and Inventory Management?
IoT devices collect and transmit data to applications, which can then use AI/ML analytics to process it. The typical applications for these two technologies in warehousing include:
- Smart shelves that automate inventory counts, enable real-time inventory tracking, and improve inventory visibility and shrinkage
- Warehouse robotics with IoT sensors and computer vision that automate routine order putaway and picking tasks
- Predictive maintenance IoT systems that detect when equipment needs preventive maintenance and thus prevent unexpected downtime
- Digital twins that are digital replicas of the warehouse and its operations, updated in real time
Among industrial-grade IoT systems, digital twins, perhaps, have the highest ROI potential. Using them, you can run simulations on potential cost-saving improvements or stress-testing critical processes without disrupting real-world operations. As a result, you can make informed decisions to refine your warehouse and inventory operations.
IoT solutions for warehouse management can use the following devices for data collection:
|
Device |
Description |
Use cases |
Pros |
Cons |
|
RFID tags |
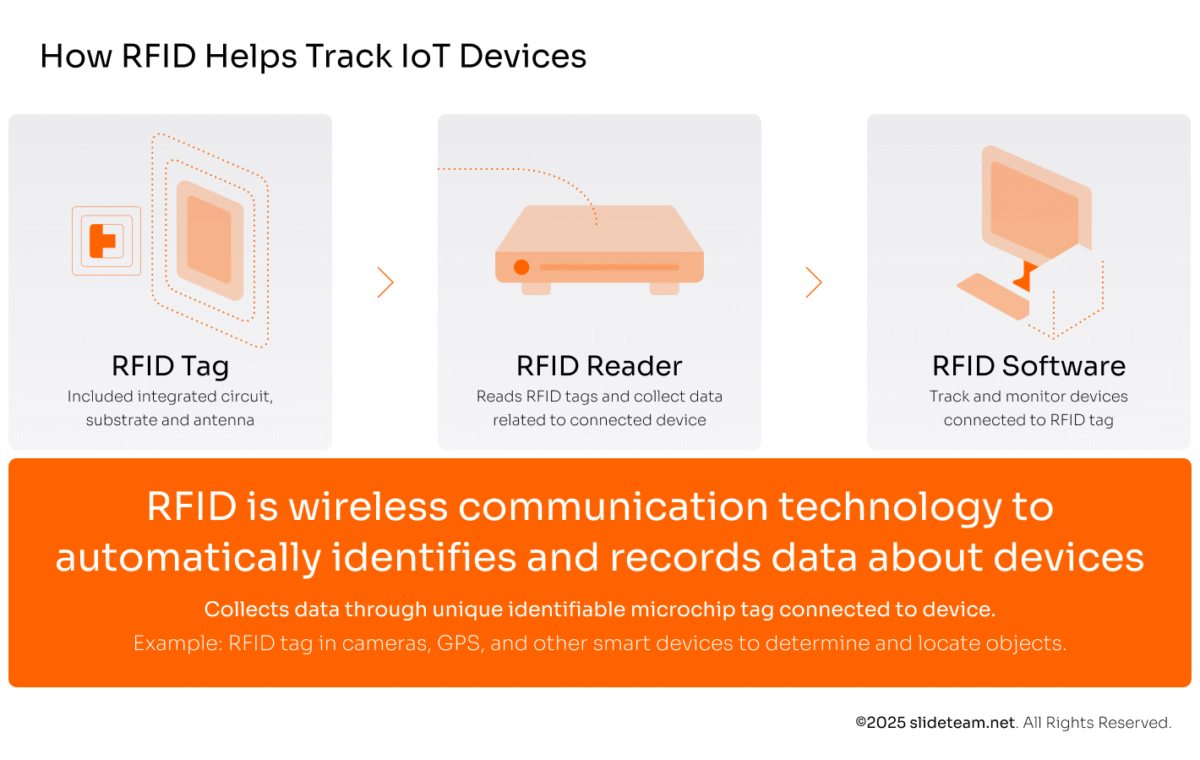
Devices that use radio frequencies to communicate the recorded data and state to readers |
|
|
|
|
BLE beacons |
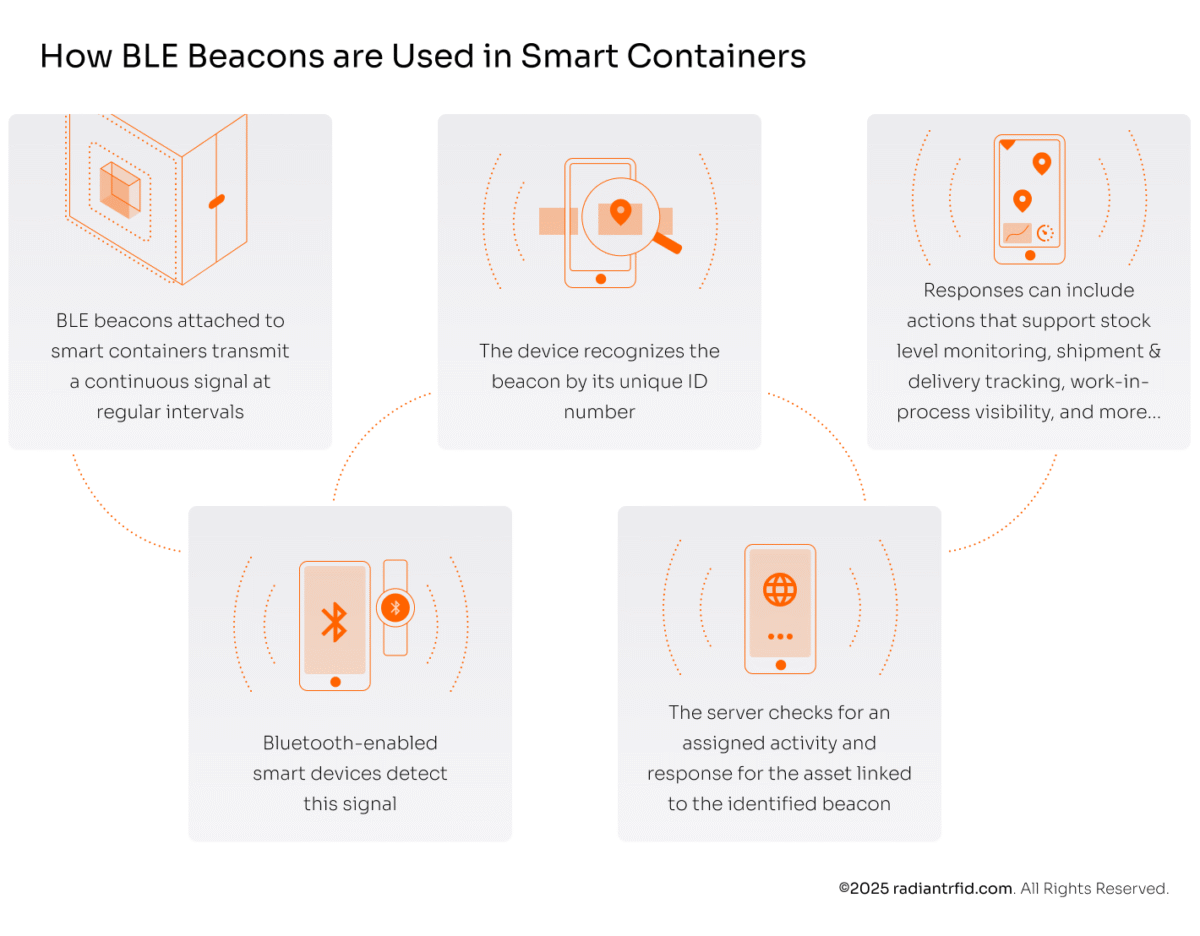
Bluetooth devices designed to minimize energy consumption and suitable for short-distance, compact data transmissions |
|
|
|
|
Computer vision systems (AI cameras) |
A network of cameras that use AI-powered computer vision to detect and identify objects and activity in real-time footage |
|
|
|
Hesitating between RFID tags, BLE beacons, and computer vision systems? We routinely help our clients select the most effective option for their warehouse IoT solutions. Get in touch with us to receive a recommendation based on your needs, operations, and challenges.
Hesitating between RFID tags, BLE beacons, and computer vision systems? We routinely help our clients select the most effective option for their warehouse IoT solutions. Get in touch with us to receive a recommendation based on your needs, operations, and challenges.
What Are the Key IoT Elements for Warehouse Automation?
An IoT warehouse management solution consists of four key layers:
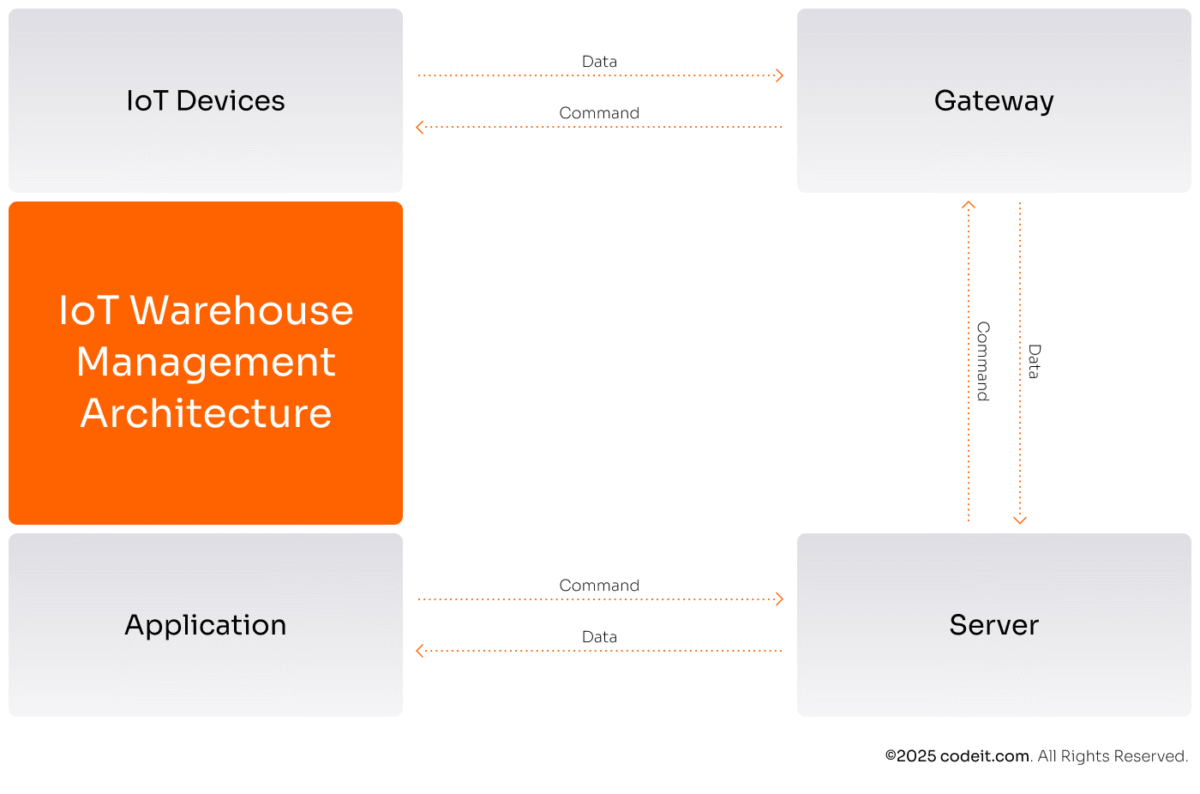
You may also add an extra layer, edge computing one (more on that below).
IoT Devices
IoT devices collect and send raw data for further processing. They can include the RFID tags, BLE beacons, AI cameras, and smart sensors. The latter can collect data on temperature, humidity, pressure (which can be used for weighing), and air quality. You can also use GPS sensors for sensor-based inventory control with live tracking and geofencing.
Which IoT devices should you choose for your IoT inventory management solution? That depends on your objectives and use cases.
For example, RFID IoT warehouse systems are more suitable for tracking large quantities of inventory items and assets in spacious warehouses. BLE beacons, in turn, are more appropriate for precise location tracking. Or, if you need an IoT cold chain management solution, you’ll need smart sensors that monitor temperature and humidity.
The most common IoT device use cases include:
- Real-time IoT asset tracking in warehouses
- Real-time inventory location tracking
- Smart shelves that monitor stock levels and send alerts when inventory is low
- Cold chain management for perishable goods (food, pharmaceuticals)
- Automated replenishment based on real-time inventory levels and AI-powered demand forecasting
For example, here’s how RFID enables tracking IoT devices:
And here’s how BLE beacons work for smart containers:
Gateways & Servers
On their own, IoT devices aren’t worth much: they have to be connected to a local network or the internet to transmit data for further analysis. So, your warehouse will have to enable that connection. Your options include:
|
Type |
Typically used for |
|
Wi-Fi network |
Smart sensors |
|
Ethernet connection |
AI cameras |
|
Bluetooth connection |
BLE beacons |
|
Cellular (4G/5G) network |
Smart sensors |
Once your IoT inventory management data travels through the gateway, it’ll have to land on the application’s servers. Those can be on-premises or in a cloud provider’s data center. Cloud offers instant scalability, lower TCO (no upfront costs for purchasing the equipment), and faster setup, which is why it’s the usual choice for IoT-based warehouse management systems.
Servers are responsible for both storing the collected IoT data and running analytics on it for user-facing applications.
Edge Computing
While most data processing takes place outside of IoT devices, some may come with embedded IoT software for analyzing the data collected. This software enables devices to process IoT data for specific tasks, make decisions, and communicate with other systems or networks.
If your warehouse is spacious, consider including an edge computing layer in your automated warehouse management system. This layer consists of edge nodes located closer to the IoT devices. They can analyze the incoming data without sending it to the central servers.
Here’s how this layer integrates into the overall IoT architecture:
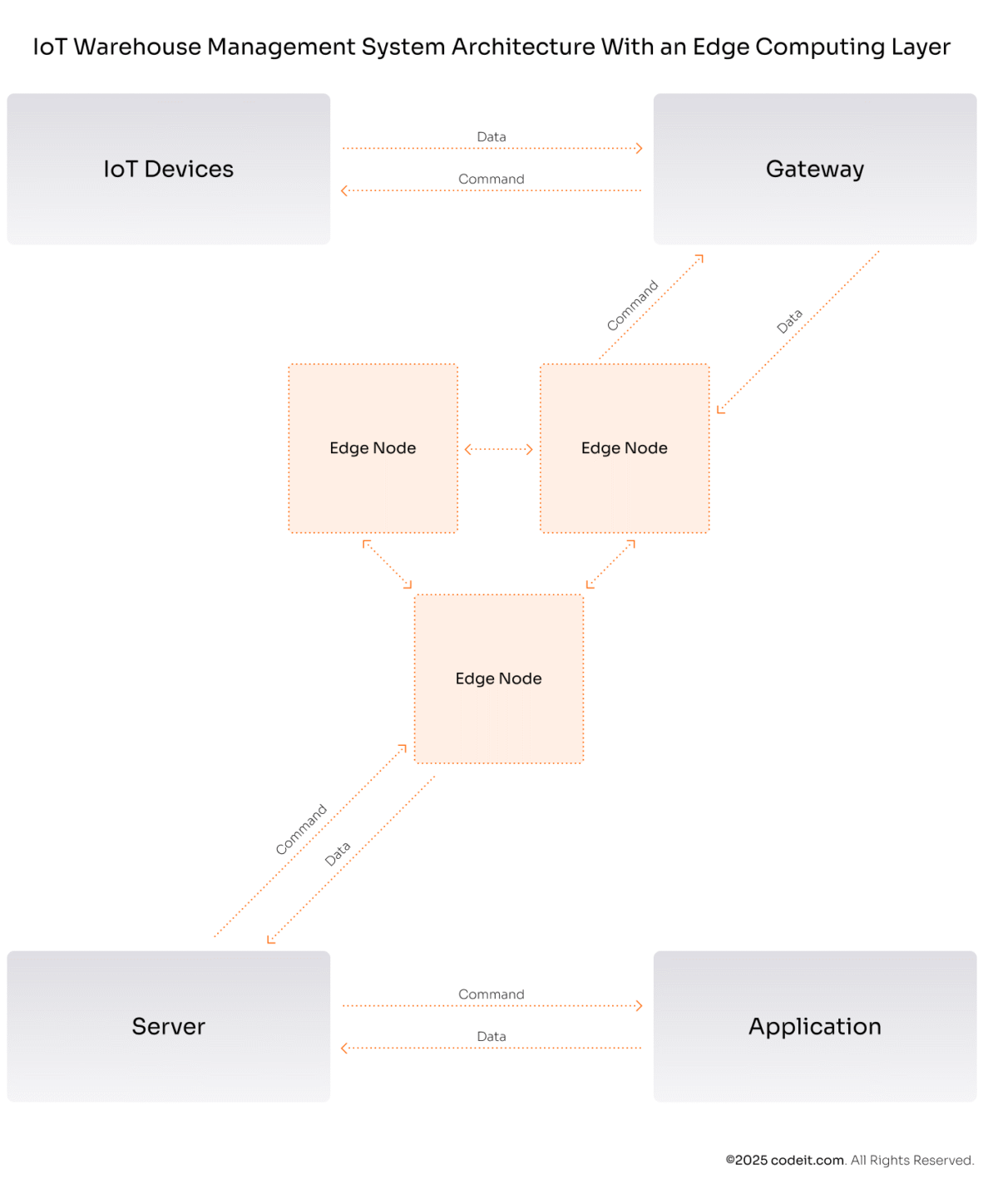
Including this layer allows you to benefit from:
- Faster data processing as the nodes analyze data only from specific sensors
- Lower load on the gateway and lower cloud costs since not all data is transferred to the servers
- Lower storage and computing costs as servers process less data
- Better scalability as adding new IoT devices doesn’t necessarily increase the load on the gateway and servers
That’s why edge computing is commonly used in industrial IoT warehouse systems that have to return real-time responses. For example, as part of a cold chain management IoT system, edge nodes can assess sensor data to evaluate temperature and send alerts only when anomalies are detected.
Application Layer
This is the user-facing component of your IoT system that receives data from the servers, visualizes it, and allows your staff to interact with it. For example, if you use IoT for inventory management, the application can visualize which shelves are full or calculate the most optimal putaway route.
Common applications include:
- Digital twins, digital replicas that enable users to run simulations and stress-test processes
- AI-powered automation systems that can automate processes like replenishment (with demand forecasting and real-time inventory data) or order pickup route planning
- Analytics systems that aggregate real-time and historical data and identify trends in it; they can be used to track metrics like putaway time, inventory turnover, and dock-to-stock cycle time
Your application layer also needs to be integrated with other systems (e.g., warehouse management system, ERP, accounting software). Seamless integration will eliminate manual data entry and improve the accuracy and range of analytics insights across your organization.
What Are the Benefits of IoT in Warehouse and Inventory Management?
Improving warehouse and inventory management using IoT and AI/ML can effectively mean minimizing shrinkage, speeding up order fulfillment, and reducing costs.
Reduced Shrinkage
Inventory shrinkage can happen for many reasons: missing shipping labels, human error when placing inventory items, and damage sustained during picking and packing. An IoT-based inventory management system can help you reduce shrinkage by:
- Providing accurate data on the location of every tagged inventory item in real time
- Comparing purchase orders with delivered items to detect shrinkage
- Alerting your staff when lost or misplaced items are detected
- Assessing item condition with computer vision to detect damaged or expired goods
IoT sensors can help you reduce inventory errors by 30%. That means not just preventing shrinkage but also speeding up the dock-to-stock cycle and order fulfillment and improving customer satisfaction.
Significant Cost Savings
Using AI/ML and IoT in warehouse management can bring down operational costs by:
- Automating processes (e.g., route planning, inventory locating, tag scanning)
- Reducing labor costs by employing autonomous robots for specific tasks (e.g., order picking)
- Mitigating the risk of errors during pickup and packing with a warehouse automation IoT platform for quality control, reducing the likelihood of returns as a result
How Yalantis Leverages IoT for a Smart Warehouse System
If you want to know how valuable IoT data can be in practice, look no further than our big data analytics platform for a US-based 3PL logistics company.
Despite having a wealth of raw data from RFID tags, IoT devices, and supply chain logs, our client struggled to turn it into valuable insights. The problems were apparent: incomplete data, ineffective analytics, and data silos all hindered effective data use.
To help the company turn raw data into actionable insights, we built a big data analytics platform consisting of a data lake, real-time data extraction layer, data visualization and analysis, and predictive analytics:
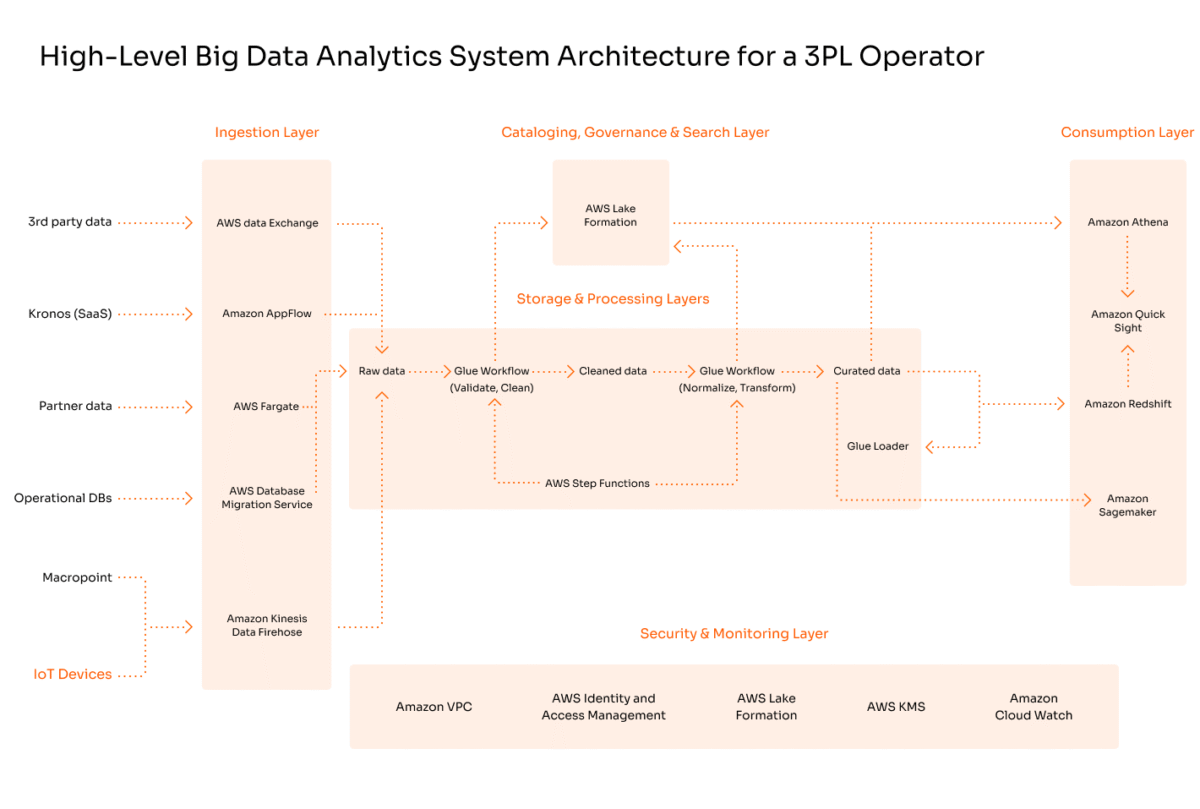
We selected the AWS tech stack for its unlimited and low-cost scalability and robust AI/ML analytics tools.
With our solution, the client could effectively track deliveries in real time using GPS sensors and RFID tags, reducing order errors and improving supply chain decision-making as a result.
5 Common Questions on IoT in Warehouse and Inventory Management
In our experience, clients usually have these five questions when they come to us to implement IoT for inventory tracking or warehouse management.
How do I ensure high performance for my IoT system?
The network, infrastructure, and data management processes can all impact the performance of IoT inventory management systems. To ensure high performance:
- Select the right network type based on data volumes and latency requirements
- Consider implementing edge computing for real-time IoT-enabled systems
- Apply data filtering and compression at the sensor layer
- Use a microservices architecture for your IoT system
- Enable autoscaling in the cloud
- Conduct thorough IoT system validation to address performance bottlenecks
How do I mitigate security risks during IoT implementation?
As we outlined in detail in our IoT vendors development guide, implementing IoT systems carries inherent security risks. IoT devices can be hacked, and their vulnerabilities can become exploits that grant unauthorized access to your other systems.
To secure the use of IoT in inventory management and warehouse operations, we:
- Enable secure boot if IoT devices support it
- Introduce reciprocal authentication
- Implement end-to-end data encryption to secure data transmission
- Ensure alignment with cybersecurity standards (e.g., IEC 62443)
What are the prerequisites for implementing IoT in Inventory Management?
Before you can implement your desired IoT inventory management system or add IoT capabilities to your warehouse management system, we advise you to:
- Define your business objectives and performance expectations
- Identify the appropriate use cases of IoT in inventory management and warehouse operations (e.g., leveraging IoT in cold chain management)
- Assess your data management practices to ensure data consistency, reliability, and interoperability
- Evaluate your network bandwidth and latency against future data transmission volumes
- Assess your infrastructure readiness to handle large volumes of raw IoT data and advanced analytics
What systems can receive data from IoT devices?
You can enhance your inventory management system using IoT data or integrate IoT devices with your warehouse management system. Alternatively, you can also feed the data into ERP systems, MES software, and analytics and BI tools.
How do I minimize risks during IoT implementation?
At Yalantis, we minimize risks during IoT product development by:
- Thoroughly assessing risks, including security risks, and devising mitigation strategies
- Using a scalable architecture to facilitate scalability and future updates
- Conducting a pilot project whenever possible
- Testing the solutions to validate their connectivity, accuracy, and performance
De-risk IoT implementation with an expert in IoT solutions
Take advantage of our 15+ years of IoT expertise to maximize your solution’s longevity, security, scalability, and ROI.
In Conclusion
The IoT technology can help you boost supply chain efficiency, order fulfillment speed, and inventory accuracy, but it needs a powerful AI/ML data analytics layer to deliver maximum ROI. After all, raw data is only as valuable as the insights you can derive from it.
Need guidance designing the most effective IoT solution for your inventory or warehouse management? Don’t have the expertise to turn your envisioned IoT ecosystem into reality? We provide the full range of IoT services to help you in either case. Reach out to our consultants to discuss how our IoT expertise can be of service.
FAQ
What warehouse operations benefit most from IoT?
In our experience, IoT in inventory management delivers high ROI as it enables real-time visibility into inventory levels and provides accurate inventory data for picking and packing. Apart from efficient inventory management, other significant benefits of the IoT technology include real-time asset tracking and monitoring, predictive maintenance for equipment, and more effective cold chain management.
How is IoT used in inventory management to improve order accuracy?
IoT inventory management solutions automate item verification with RFID tags, BLE beacons, or AI cameras. This eliminates the need for manual scanning, inherent to traditional inventory management methods, and mitigates the risk of human error. Smart shelves, in turn, can detect stock removal and immediately alert staff if someone picks the wrong item.
Do I need a custom IoT solution or an off-the-shelf one?
The answer depends on your use cases, objectives, technical requirements, and available budget. In general, a custom IoT-based warehouse management system is a more suitable choice if you have unique requirements, integration needs, or security constraints. That’s typically the case for large-scale, multi-location warehousing operations and highly regulated industries.





